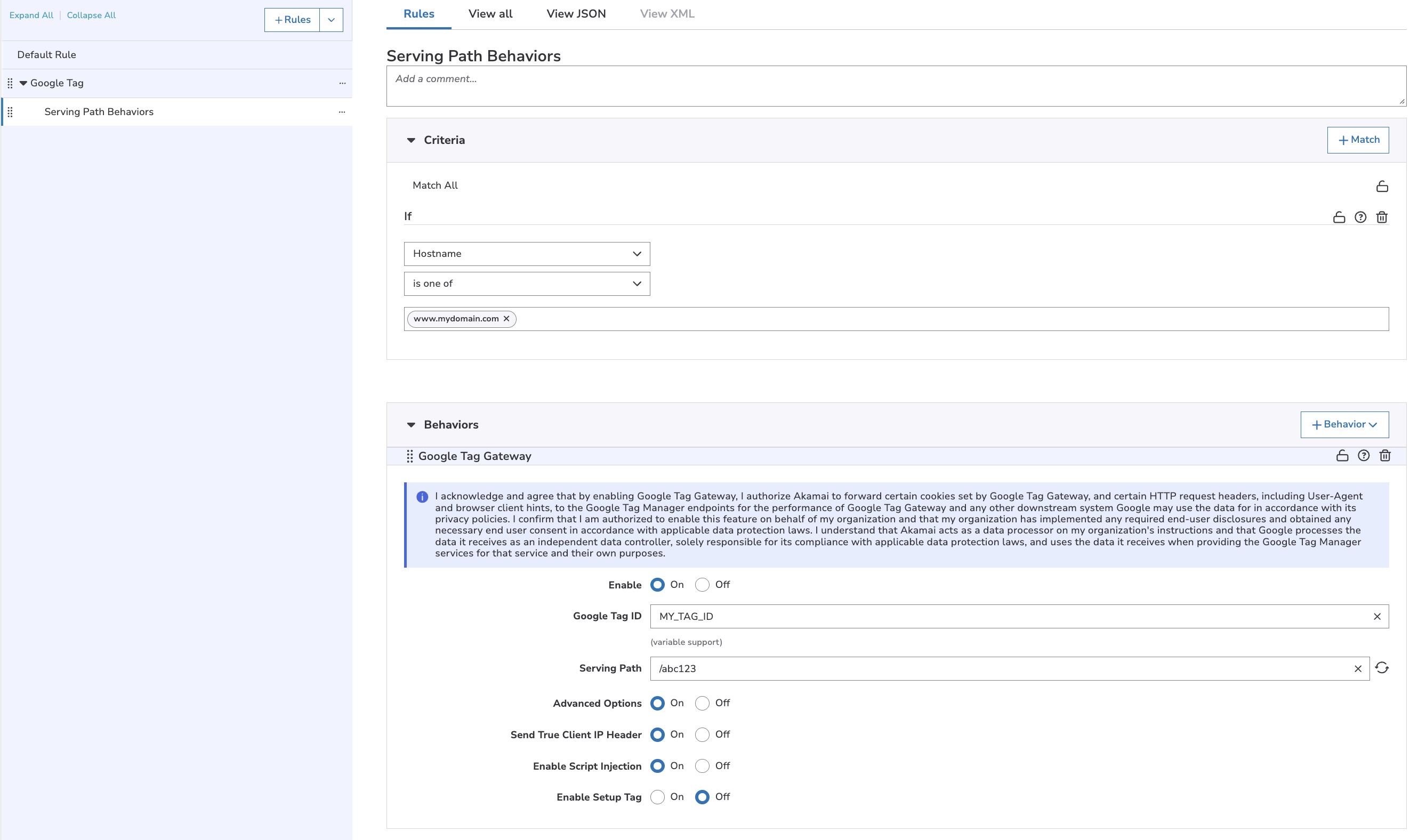
Google Tag Gateway
This behavior allows you to deploy and deliver Google Tags from within your existing property, mitigating third-party tracking limitations enforced by modern browsers.
Before you begin
Note that once you provide all the required data in the behavior, we ask you to acknowledge the following mandatory legal disclaimer:
I acknowledge and agree that by enabling Google Tag Gateway, I authorize Akamai to forward certain cookies set by Google Tag Gateway, and certain HTTP request headers, including User-Agent and browser client hints, to the Google Tag Manager endpoints for the performance of Google Tag Gateway and any other downstream system Google may use the data for in accordance with its privacy policies. I confirm that I am authorized to enable this feature on behalf of my organization and that my organization has implemented any required end-user disclosures and obtained any necessary end user consent in accordance with applicable data protection laws. I understand that Akamai acts as a data processor on my organization's instructions and that Google processes the data it receives as an independent data controller, solely responsible for its compliance with applicable data protection laws, and uses the data it receives when providing the Google Tag Manager services for that service and their own purposes.
How it works
Use this behavior to set up a path on your domain as a relay to Google's tag endpoints. It allows your site to load and use Google Tags as if they were on your own domain.
A correct setup of Google Tag Gateway has:
- Property rule(s) with behavior to configure the path used as the tag endpoint.
- Tags injected on page(s) of your site. Either by Property Manager, EdgeWorkers, or your own tag management solution. That uses the configured path. See Tag injection.
While an out-of-the-box Google Tag uses https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtag/js?id=TAG_ID as its SRC script, with Google Tag Gateway configured, you replace that with your configured path. For example, https://my.domain.com/abc123.
Note that only one instance of the behavior is allowed in a particular rule. If there are multiple rules in the property, each with an instance of the behavior, only the last rule that matches the incoming request is applied.
Features and options
| Field | What it does |
|---|---|
| Enable | Enables the Google Tag Gateway behavior. |
| Google Tag ID | Specifies the unique Google Tag ID that was provided to you by Google. |
| Serving Path | Specifies the path that serves the Google Tag. It must consist of 6-10 alphanumeric characters and start with a slash ( / ), and must be a unique path which is not used elsewhere on your site. |
| Send True Client IP Header | Sends the True Client IP header to the Google origin. |
| Enable Script Injection | Injects the Google Tag script directly into the page. Enable this if your pages don't already include the Google Tag script. |
| Enable Setup Tag | Controls whether the injected tag should override any on-page configuration. Enable this if your pages don't already include the Google Tag script. |
Implementation
- Log into Control Center.
- Search for a property you want to add the Google Tag Gateway behavior to by entering its name into the search field or create a new property.
To get to know the stages of setting up your property, see Workflow overview.
- To add the Google Tag Gateway behavior to your property or include, see Use cases.
The Google Tag Gateway behavior is incompatible with the Brotli Support, Construct Response, and EdgeWorkers behaviors.
- Activate on staging. Deploy your property version on the servers in the Akamai Edge Staging Network (ESN) so that you can test the configuration.
- Test on staging. Set up and run tests against the staging configuration. Once you confirm that your configuration works fine, you can perform regression and load testing, if needed, outside of Property Manager.
- Activate on production. Deploy your configuration version to the Akamai Production network to prepare to go live.
Use cases
Single Google Tag
- Add a rule called Google Tag with at minimum a Hostname match.
- Add and configure the Google Tag Gateway behavior, specifying the Google Tag ID (provided by Google) and Serving Path.
- In the Advanced options, choose whether you want to inject the tag automatically with Akamai, or if you inject the tag using another platform. See Tag injection.
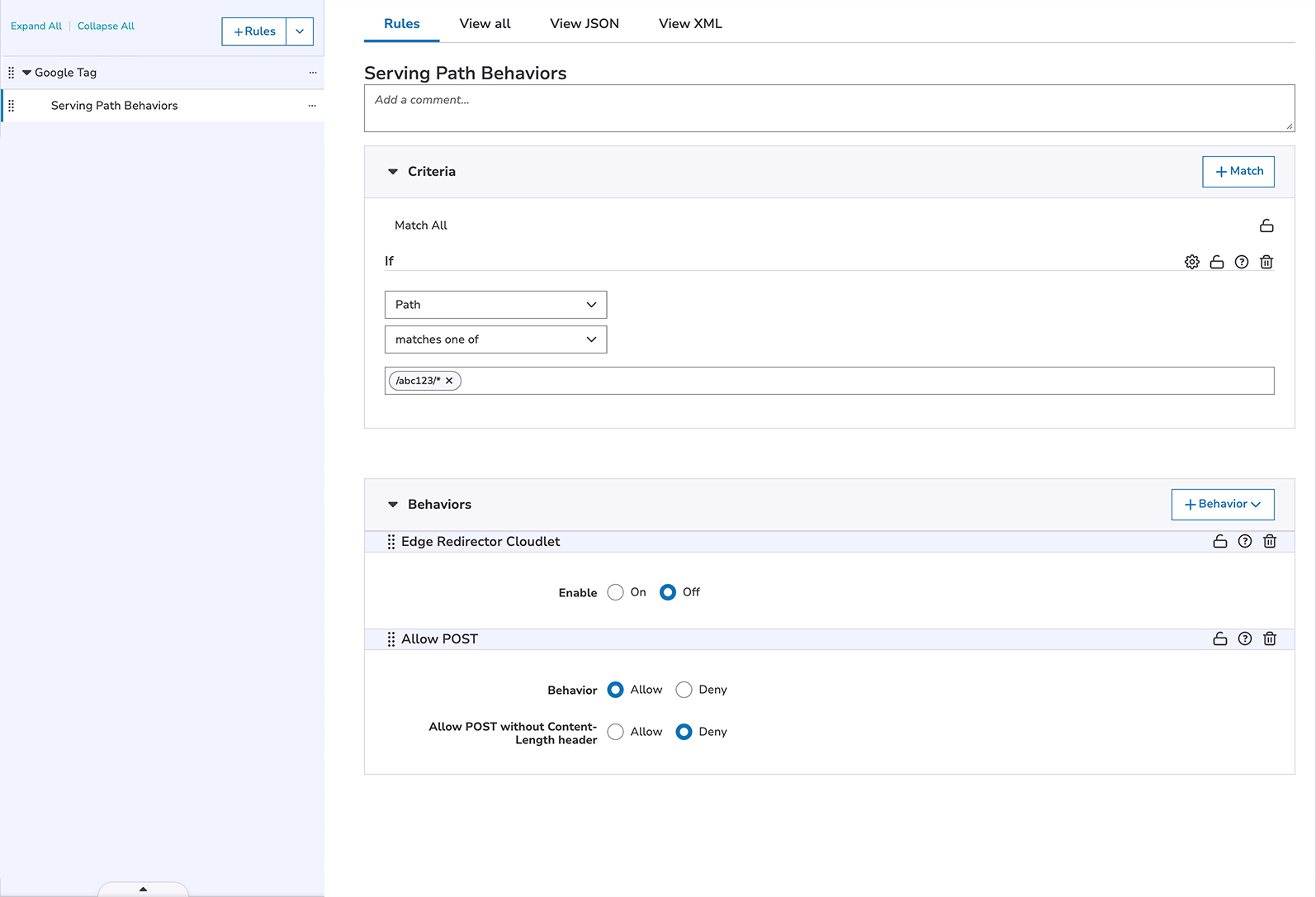
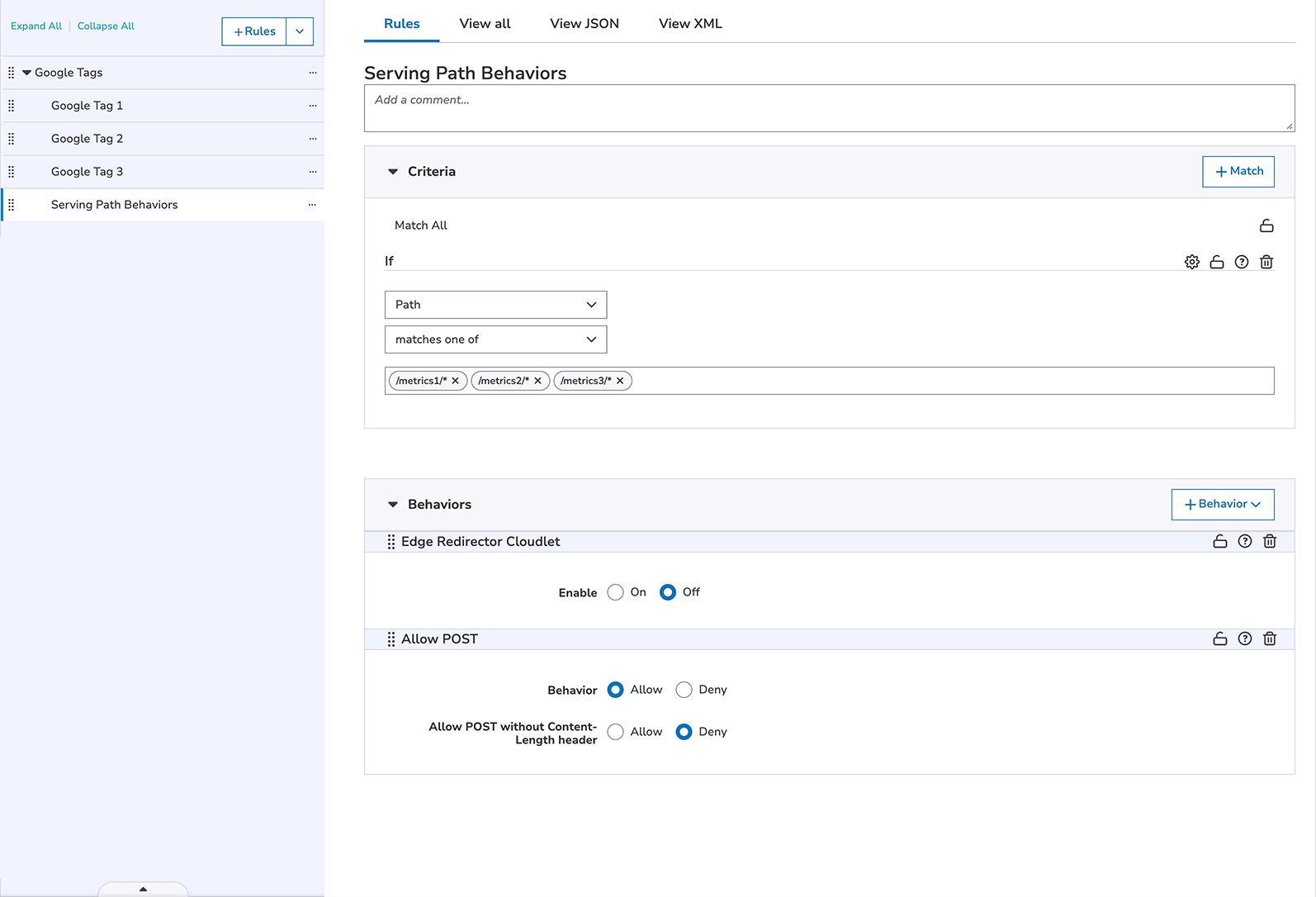
- Add a child rule matching all sub-paths of the tag's Serving Path. For example,
/metrics/*, with behaviors to:- Disable Edge Redirector Cloudlet if enabled within the configuration.
- Disable Edge Redirector Cloudlet if enabled within the configuration.
- Allow POST requests.
Multiple Google Tags
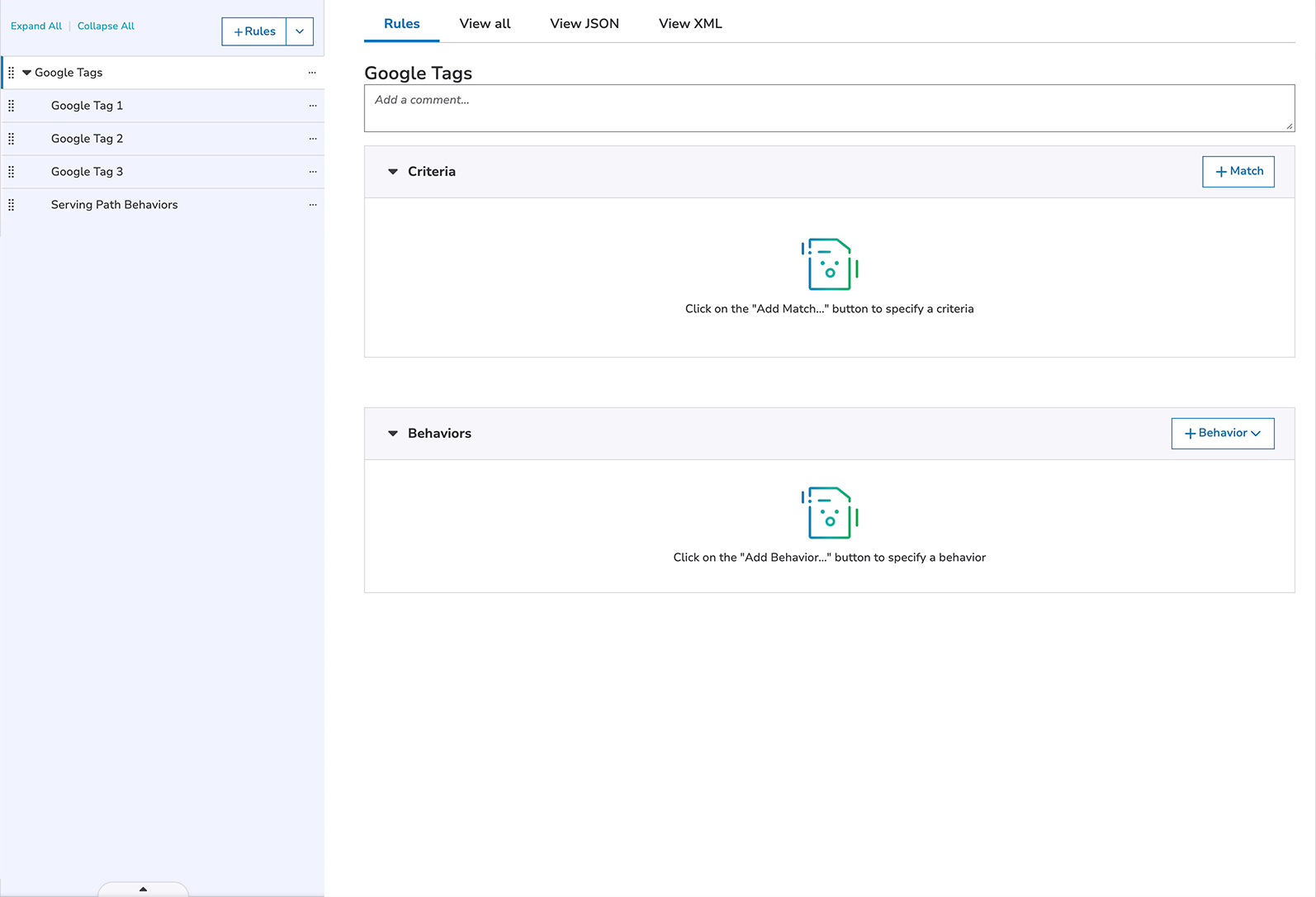
To set up multiple Google Tags, you need to configure a separate rule for each Google tag with the Google Tag Gateway behavior in each rule.
- Add a parent rule with no match criteria. For example, My Google Tags.
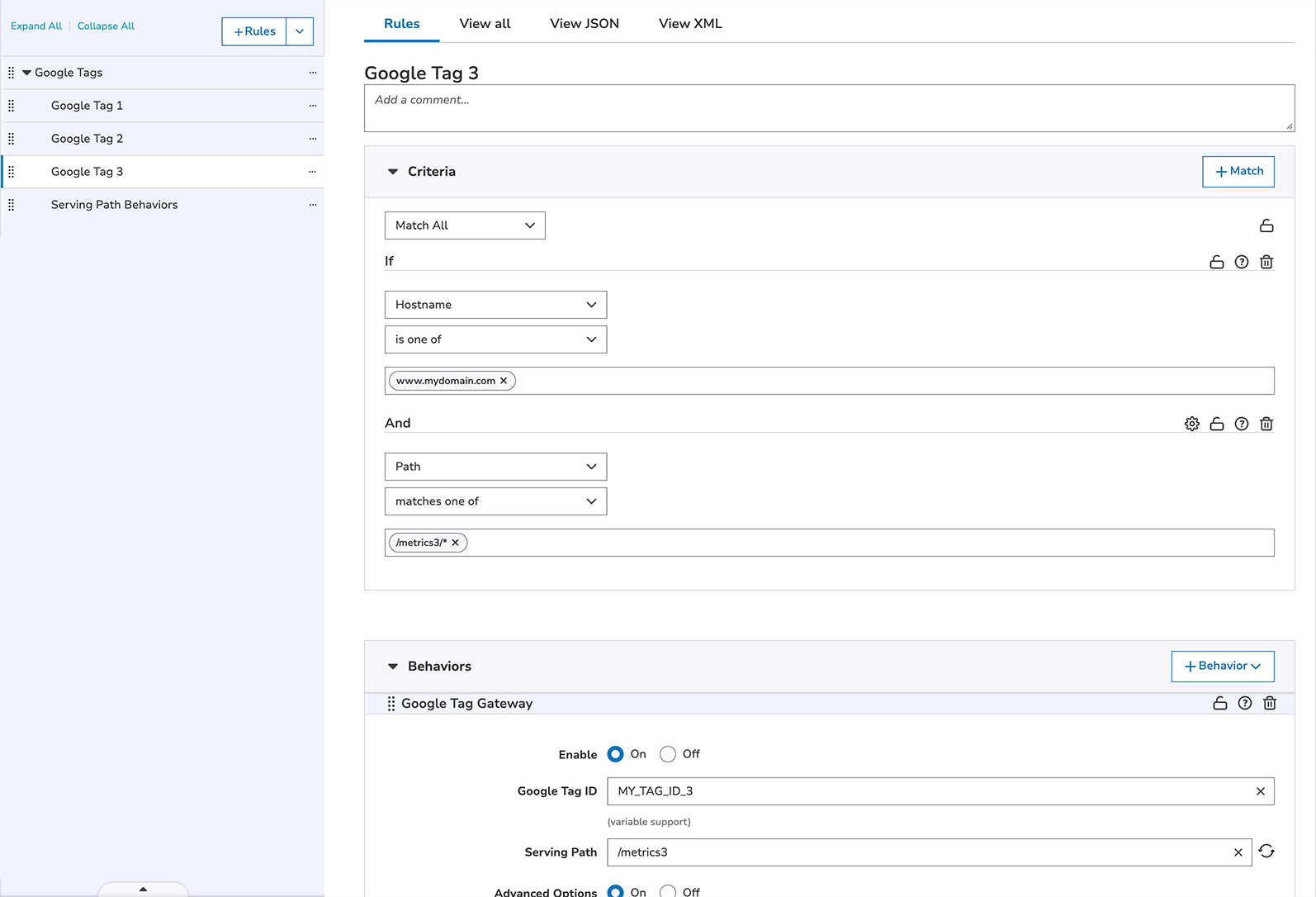
- Add child rules for each Google Tag. Each rule should match only for the intended hostname and Serving Path.
- To each child rule, add and configure the Google Tag Gateway behavior.
- Specify the Google Tag ID (provided by Google) and Serving Path.
- Make sure that both Enable Script Injection and Enable Setup Tag options are set to Off.
- Add a child rule matching wild-card sub-paths to Serving Paths. For example,
/metrics1/*, /metrics2/*that includes behaviors to:- Disable Edge Redirector Cloudlet if enabled within the configuration.
- Disable Edge Redirector Cloudlet if enabled within the configuration.
- Allow POST requests.
You can’t use the behavior's Script Injection option to inject more than one tag on any given page.
Tag injection
Google Tags need to be included on the page. You have several options for injecting the tag through, depending on your requirements:
- Akamai. Enable the Enable Script Injection option under Advanced Options in the GTG behavior. The Akamai CDN will add the
<script>tag to your HTML page responses before sending them forward to the client. You can inject only one tag per-page using this method. - Google Tag Manager. Use Google Tag Manager, Adobe Launch, or other system to inject the tags, just as with any other third-party tag. Replace the URL in the out-of-the-box Google Tag snippet with the URL and a path configured by the behavior.
- Direct editing. You can use any CMS to add your tags directly to the HTML of your pages. Replace the URL in the out-of-the-box snippet with the URL and a path configured by the behavior.
Tag Injection Guidance
If your website uses multiple Google Tags or a tag management solution, we recommend managing tag injection directly within your existing platform rather than through Akamai.
When you inject more than one Goole Tag at the page level in your property, only a single tag can take effect. To avoid unexpected behavior when using multiple Google Tags, you should rely on your tag manager or application platform to control how and when tags are injected.
We also don’t recommend Akamai-based tag injection when using a Consent Management Platform (CMP) alongside a tag manager. Injecting Google Tags outside of your existing workflow may bypass or override your consent settings, which could impact your privacy and compliance controls. Managing tags within your tag manager ensures that your consent preferences are always respected.
As a best practice, the Enable Tag Setup option should remain disabled. This setting is not required for the existing Google customers using Google Tag Gateway and keeping it disabled helps ensure seamless integration with your current tag management and consent frameworks.
If you have questions about the best configuration for your environment, contact Akamai support to help you determine the optimal setup.
Products that use this behavior
You can create a custom rule and configure the Google Tag Gateway behavior inside a hostname match for the Ion, Dynamic Site Accelerator, and API Acceleration products.
Updated 18 days ago
