Get started with Longview
To start using Longview to capture metrics from a Linux server, you need to create a new Longview Client instance and install the Longview Agent on that server.
- Create a Longview Client
- SSH into the Linode
- Install the Longview Agent
- Start the Longview Agent
- View Longview Client Statistics
Create a Longview client
-
Log in to Cloud Manager and click on the Longview link in the sidebar.
-
On the Longview Clients page, click on the Add a Client link on the top right-hand corner. This creates a Longview Client instance.
-
The new Longview Client instance is displayed along with its auto-generated label, its current status, installation instructions, and API key. Its status should be "Waiting for data" as you have not yet installed the Longview agent on your Linux system.
The displayed
curlcommand is used in the next section to install the Longview agent on the desired Linux system. The long string appended to the urlhttps://lv.linode.com/is your Longview Client instance's GUID (globally unique identifier).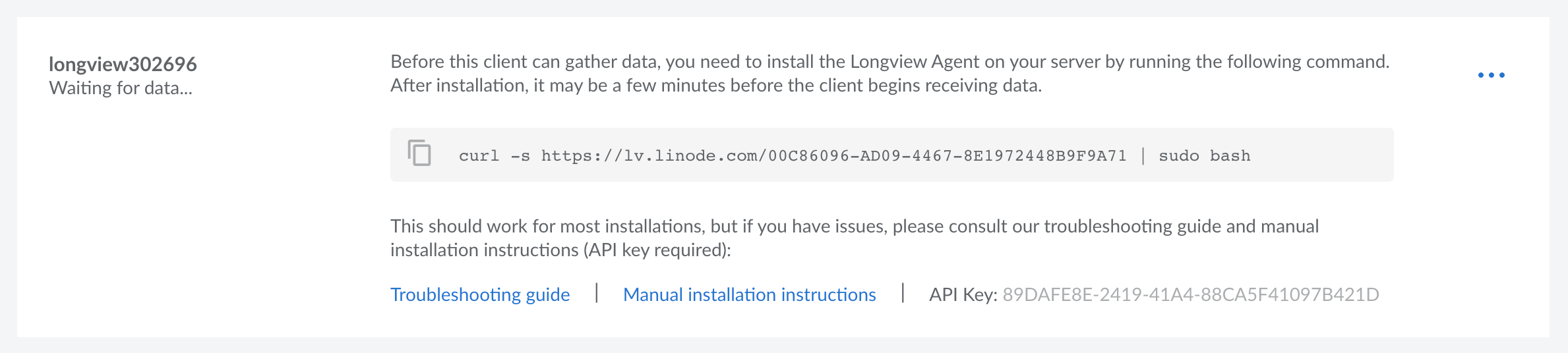
SSH into the Linode
-
Open a terminal on your local computer and log in to your Linode (or other Linux system) over SSH. In the command below, replace [user] with your remote username and [ip-address] with the IP address or fully qualified domain name of your Linode. See Managing IP Addresses on a Linode.
ssh [user]@[ip-address] -
Switch to the
rootuser.su - root
Install the Longview agent
Automatic installation
Run the Longview Client instance's curl command on your Linux system. The installation will take a few minutes to complete.
Ensure you replace the example
curlcommand below with your own Longview Client instance's GUID.
curl -s https://lv.linode.com/05AC7F6F-3B10-4039-9DEE09B0CC382A3D | sudo bash
Possible error messages (and how to overcome them)
-
Lock error: This likely means that another program is attempting to update or install packages on your system. To overcome this error, you can delete the current Longview Client, wait a few minutes, create a new Longview Client, and try the installation process again.
E: Could not get lock /var/lib/dpkg/lock-frontend. It is held by process 12549 (apt-get) N: Be aware that removing the lock file is not a solution and may break your system. E: Unable to acquire the dpkg frontend lock (/var/lib/dpkg/lock-frontend), is another process using it? -
Invalid installer session error: To overcome this error, delete the current Longview Client, create a new one, and try to install the Longview Agent again.
Invalid Installer Session Please see the Longview details page to start a new session -
OS release file not found error: To overcome this error, go through the manual installation instructions. In the
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/longview.listfile for Debian and Ubuntu, and in the/etc/yum.repos.d/longview.repofile for CentOS, update the last supported version as the following:focalfor Ubuntubullseyefor Debian8for CentOS
Err:7 https://apt-longview.linode.com bookworm Release
404 Not Found [IP: 2600:3c03::f03c:91ff:feba:159b 443]
E: The repository 'https://apt-longview.linode.com bookworm Release' does not have a Release file.
E: Unable to locate package linode-longview
Err:7 https://apt-longview.linode.com noble Release
404 Not Found [IP: 2600:3c03::f03c:91ff:feba:159b 443]
E: The repository 'https://apt-longview.linode.com noble Release' does not have a Release file.
E: Unable to locate package linode-longview
If you are not able to overcome these error messages, follow the manual installation instructions below.
Manual installation
If the automatic installation instructions failed, you can also manually install the Longview Agent on CentOS, Debian, and Ubuntu. Other distributions, like Fedora and Alpine Linux, are not officially supported.
-
Add a configuration file to store the repository information for the Longview agent:
-
Debian and Ubuntu:
Find the codename of the distribution running on your Linode.
root@localhost:~# lsb_release -scstretchUsing the text editor of your choice, like nano, create a custom sources file that includes Longview's Debian repository and the Debian distribution codename. In the command below, replace stretch with the output of the previous step.
deb https://apt-longview.linode.com/ stretch main -
CentOS:
Using the text editor of your choice, like nano, create a
.repofile and copy the contents of the example file below. ReplaceREVin the repository URL with your CentOS version (e.g., 7). If unsure, you can find your CentOS version number withcat /etc/redhat-release.[longview] name=Longview Repo baseurl=https://yum-longview.linode.com/centos/REV/noarch/ enabled=1 gpgcheck=1
-
-
Download the repository's GPG key and import or move it to the correct location:
-
Debian and Ubuntu:
sudo curl -O https://apt-longview.linode.com/linode.gpg sudo mv linode.gpg /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/linode.gpg -
CentOS:
sudo curl -O https://yum-longview.linode.com/linode.key sudo rpm --import linode.key
-
-
Create a directory for the API key:
sudo mkdir /etc/linode/ -
Copy the API key from the Installation tab of your Longview client's detailed view in the Cloud Manager. Put the key into a file, replacing the key in the command below with your own.
echo '266096EE-CDBA-0EBB-23D067749E27B9ED' | sudo tee /etc/linode/longview.key -
Install Longview:
-
Debian and Ubuntu:
sudo apt update sudo apt install linode-longview -
CentOS:
``` sudo yum install linode-longview ```For Debian and Ubuntu, update the
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/longview.listfile withfocalfor Ubuntu andbullseyefor Debian. For CentOS, update the REV value in/etc/yum.repos.d/longview.repoto the last supported version, which is8. This is a temporary workaround until the latest version of the Longview package is released.
-
Start the Longview agent
Once the installation is complete, verify that the Longview agent is running:
sudo systemctl status longview
You should see a similar output:
-
Debian and Ubuntu:
● longview.service - LSB: Longview Monitoring Agent Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/longview; generated; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Mon 2019-12-09 21:55:39 UTC; 2s ago Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8) Process: 2997 ExecStart=/etc/init.d/longview start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Tasks: 1 (limit: 4915) CGroup: /system.slice/longview.service └─3001 linode-longview -
CentOS:
● longview.service - SYSV: Longview statistics gathering Loaded: loaded (/etc/rc.d/init.d/longview; bad; vendor preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Tue 2019-12-10 22:35:11 UTC; 40s ago Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8) CGroup: /system.slice/longview.service └─12202 linode-longview Dec 10 22:35:11 203-0-113-0.ip.linodeusercontent.com systemd[1]: Starting SYSV: Longview statistics gathering... Dec 10 22:35:11 203-0-113-0.ip.linodeusercontent.com longview[12198]: Starting longview: [ OK ] Dec 10 22:35:11 203-0-113-0.ip.linodeusercontent.com systemd[1]: Started SYSV: Longview statistics gathering.
If the Longview agent is not running, start it with the following command:
sudo systemctl start longview
View Longview client statistics
Switch back to Cloud Manager's Longview Clients page in your browser and verify that system information and metrics have started to appear. To learn more about the metrics available on Longview, see Understanding Longview Metrics.

It can take several minutes for data to load and display in Cloud Manager.
Updated 8 months ago
