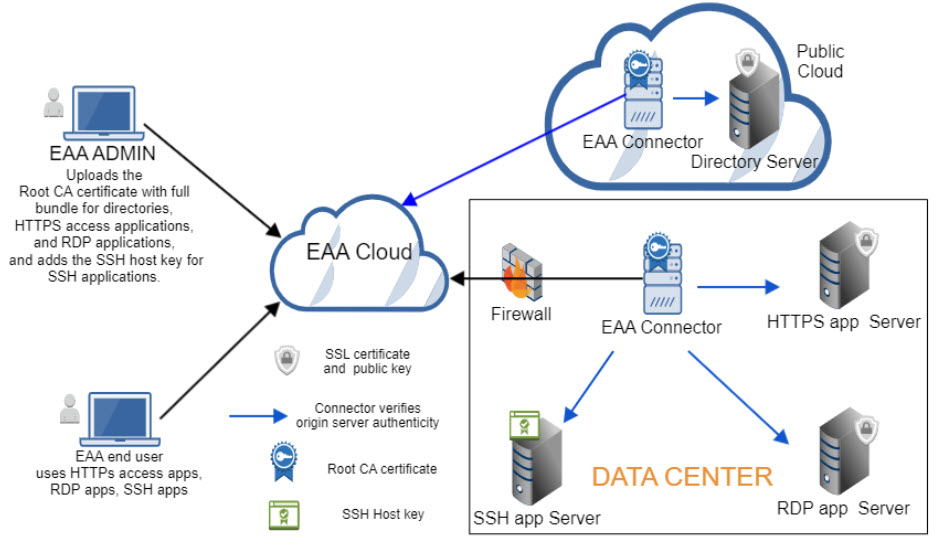
Certificate-based validation of origin servers
Validate with a certificate for directory server and application server (for HTTPS, RDP and SSH applications). As a leader in Zero-Trust security, Enterprise Application Access doesn't trust anyone or any device. As directories and applications migrate from your data center to public clouds, the EAA connector does certificate validation of the origin servers, using industry standard - TLS technology, mitigating any man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks. The origin server can be a directory service like AD, LDAP, AD LDS, an application server for an HTTPS web application, an application server for a RDP application, or an application server for a SSH application.
Enterprise Application Access customers can also leverage this enhanced security while communicating with the origin servers which may continue to reside within your data center. The EAA connector inside the data center validates the authenticity of the origin server and improves the security posture.
Note
Certificate based origin server validation is optional and can be disabled.
The workflow for enabling origin server certificate validation depends on the type of service:
-
Directory origin server validation:
-
Enable server certificate verification and select this certificate to do origin server validation while configuring your directory and save the directory. Also see Directory server certificate validation rules and use cases for configuring Host and Host Aliases fields.
This enables the connector to validate the directory before doing any services like adding authenticated users to the directory, updating groups in directories.
-
HTTPS origin server validation:
-
Upload the ROOT CA certificate with the full bundle for the web application server into EAA.
-
Enable server certificate verification and select this certificate to do origin server validation while configuring your HTTPS application and deploy it. Note that if you enable server certificate verification and do not select any root CA certificate, the public CA certificates available in the connector are used to validate the origin server. If the origin server is not signed by the public CA, server certificate validation fails. Users are not able to access the web application securely.
This enables the connector to validate the HTTPS origin server using SSL protocol. Then, users can access the HTTPS access application.
-
Origin server certification validation is not done for HTTP applications.
-
RDP origin server validation:
-
Upload the ROOT CA certificate with the full bundle for the RDP server into EAA.
-
Enable server certificate verification and select this certificate to do origin server validation while configuring your RDP application and deploy it. Note that if you enable server certificate verification and do not select any root CA certificate, the public CA certificates available in the connector are used to validate the origin server. If the origin server is not signed by the public CA, server certificate validation fails. Users are not able to access the RDP application securely.
This enables the connector to validate the RDP origin server with SSL protocol. Then, the user can access the RDP application.
-
-
SSH origin server validation:
Add the SSH host key while configuring your SSH application and deploy it.
This enables the connector to validate the SSH origin server with SSL protocol. Then the user can access the SSH application. If no SSH host key is added while configuring the SSH application, then SSH server validation is not done.
Origin server validation is not done for VNC applications, SaaS applications and client-access applications.
Upload a ROOT CA certificate for origin server validation
If you want the EAA connector to do validation of the origin server for your directory service, web server hosting HTTPS applications, RDP server hosting the RDP application, you need to upload a root CA certificate with the full bundle of all the subordinates. All communication between the Enterprise Application Access connector and the origin server is done with TLS protocol, preventing man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks.
-
Log in to Enterprise Center.
-
In the Enterprise Center navigation menu, select Application Access > Certificates > Certificates.
-
Select Certificate Authorities >Add New Certificate.
-
In Name type a unique name for the certificate.
-
Click Choose File to locate and select the ROOT CA certificate file with the full bundle. For full bundle, the order must first be the server public certificate, followed by the public certificate of the intermediary, followed by the public certificate of the root CA.
-
Click Save.
Next:
-
To assign the certificate to the directory origin server see Add or edit an LDAP, AD or AD LDS directory.
-
To assign the certificate to the web application (HTTPS) origin server see Configure access parameters for an application.
-
To assign the certificate to the RDP origin server see Configure and deploy a remote desktop application.
Updated 11 months ago
