Enable DNS Protection in China
You can use SIA to directly resolve DNS traffic in mainland China. As a SIA administrator, you create a tenant for China and then enable DNS protection in that tenant. When the DNS protection setting is enabled, SIA servers in China resolve DNS traffic. This eliminates latency that your organization may experience when it uses DNS servers that are located outside of China for resolution.
The Enable DNS Protection in China setting is available from the Connection Info page of the tenant. For instructions on enabling this capability, see Enable DNS protection in China.
To direct traffic to SIA in China, a tenant administrator must either deploy Security Connector as a DNS Forwarder in the network or deploy Zero Trust Client 5.3 or later on user devices. If you deploy Zero Trust Client, you must set it up for Threat Protection. For more information on these components, see Security Connector as a DNS forwarder and the Zero Trust Client documentation.
DNS protection in China is currently in beta. To participate in the beta, contact your Akamai representative.
With this implementation, you can:
-
Isolate DNS traffic in China. SIA in China uses domains for services that are specific to China, allowing a SIA configuration and user traffic to be restricted to the regions of China. SIA also uses different tokens and other cryptographic material to secure and separate traffic in mainland China from traffic that’s handled by the global SIA solution.
-
Deploy configuration settings and policies in China. The tenant SIA configuration and deployments only apply to locations in China.
-
Prevent the logging or reporting of personal identifiable information (PII). No PII is included in logs or SIA reports.
Make sure the tenant administrator you assign to the tenant is not a SIA administrator. If you assign a tenant administrator who is also a SIA administrator, the user will lose SIA administrator privileges.
The following graphics illustrate this implementation.
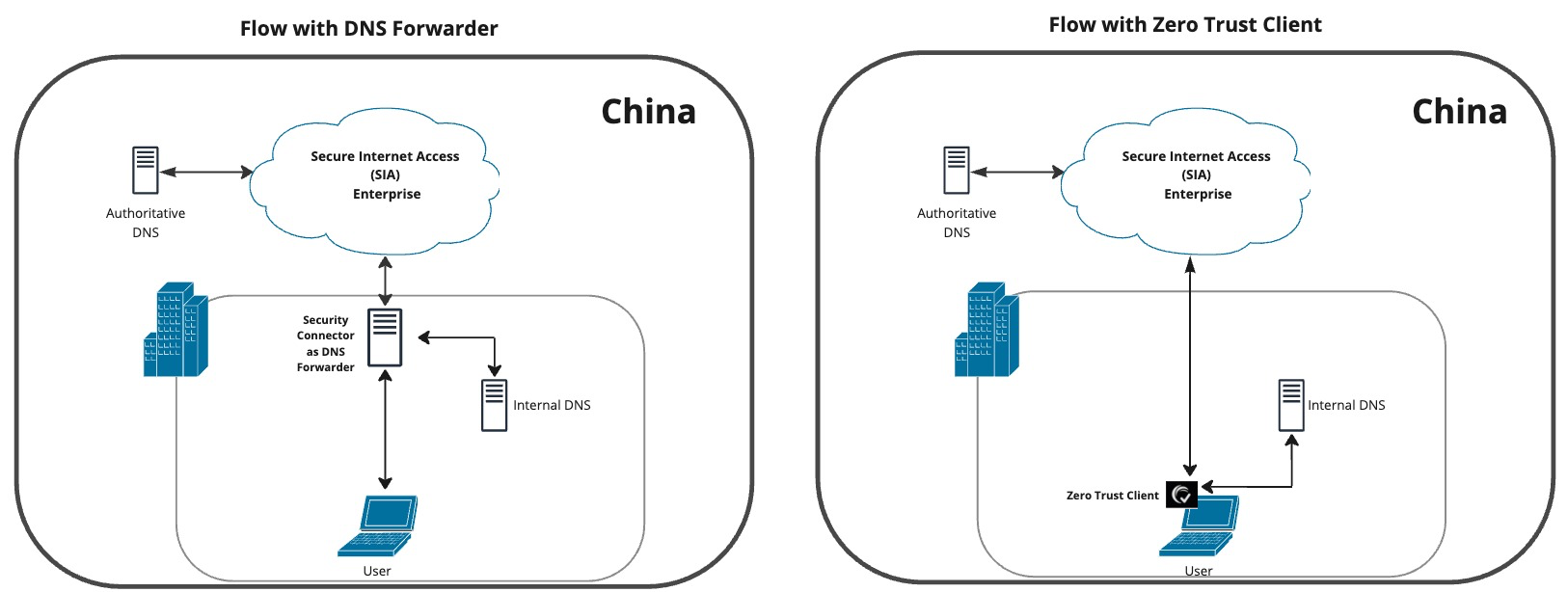
In this graphic:
-
DNS Forwarder or Zero Trust Client (ZTC) with the Threat Protection service receives all requests and then forwards internal requests to the internal DNS resolver.
Requests to internal domains are directed to a local DNS resolver based on the tenant administrator’s configuration of the Local Bypass Settings.
SIA uses services that are specific to China. This allows tenant administrators to create and deploy policies, as well as other configurations to locations in China without directly communicating with the global SIA solution.
-
External DNS requests are directed to SIA. DNS Forwarder or ZTC uses DoT to securely communicate with SIA resolvers in China. No PII is logged in SIA reports.
Limitations
These features are not supported:
- Security Connector as an HTTP Forwarder or as a Sinkhole. This implementation supports Security Connector as a DNS Forwarder only.
- SIA Proxy. In a policy, you enable DNS Only as the policy type. You cannot enable DNS protection in China if there are policies in the tenant that use the proxy.
- Identity providers. Identity providers and the features related to it such as identity connectors and directories are not supported with multi-tenancy or when the proxy is disabled. As a result, these features are not supported with SIA in China.
- IP Anycast. IP Anycast for SIA is not supported in China. However, it is supported outside of China.
- Internal IP address logging. The internal IP address of a device is not logged in SIA reports or logs.
SIA in China requires a tenant. This feature is not supported on the parent of the tenant.
Enable DNS protection in China
Complete these steps to enable DNS protection for China in a tenant. As a SIA administrator, you must view the tenant in SIA and enable the DNS protection setting while you’re in the tenant view. For more information on multi-tenancy, see Multi-tenancy.
If you plan to use DNS Forwarder, make sure you enable DNS protection in China before you set up a security connector as a DNS Forwarder. If Security Connector as a DNS Forwarder is activated before you enable DNS protection in China, it can take up to one hour before Security Connector forwards traffic to servers in China.
DNS protection in China is currently in beta. To participate in the beta, contact your Akamai representative.
Before you begin:
- If you have not done so already, create the tenant that you want to use for China. For instructions, see Create a tenant.
- Make sure that the policies in the tenant do not have the proxy enabled. This means the policy type must be DNS Only.
- Make sure there are no pending deployment changes for the tenant. If there are pending changes, deploy them.
To enable DNS protection in China:
-
View SIA as the tenant where you want to enable DNS protection for China:
-
At the top of Enterprise Center, click the Filter data by tenant option.
-
In the field that appears, select the tenant for mainland China.
-
Click OK. You are now viewing the tenant.
-
-
In the Threat Protection menu of Enterprise Center, select Clients & Connectors > Connection Info.
-
Turn on the toggle for Enable DNS Protection in China. A dialog appears to confirm that you want to enable this feature.
-
Click Yes.
Next Steps
Make sure the tenant administrator sets up a security connector as a DNS Forwarder or ZTC for Threat Protection. For more information, see Set up the security connector and Set up Zero Trust Client.
Disable DNS Protection in China
Complete this procedure if you no longer want a tenant to provide DNS protection in China.
Before you begin:
Make sure there are no pending deployment changes for the tenant. If there are pending changes, deploy them.
To disable DNS protection in China:
-
View SIA as the China tenant:
-
At the top of Enterprise Center, click the Filter data by tenant option.
-
In the field that appears, select the tenant for mainland China.
-
Click OK. You are now viewing the tenant.
-
-
In the Threat Protection menu of Enterprise Center, select Clients & Connectors > Connection Info.
-
Turn off the toggle for Enable DNS Protection in China. A dialog appears to confirm that you want to disable this feature.
-
Click Yes.
Updated almost 2 years ago
