Set up proxy chaining
SIA proxy can act as a full web proxy that performs URL filtering and anti-malware scanning in your current network configuration. Proxy chaining allows you to forward traffic from your enterprise on-premises proxy to Akamai SIA Proxy. While forwarding DNS resolvers to SIA directs malicious and risky traffic to SIA Proxy, proxy chaining further allows your organization to direct all HTTP and HTTPS traffic to SIA Proxy and scan it for malware.
In addition to enabling the proxy in a policy, enable these settings:
-
Trust X-Forwarded-For (XFF) header. The XFF contains the client IP address. It prevents users from anonymizing their IP address or configuring their browser to inject a fake XFF with a fake IP address. You should select the Trust X-Forwarded-For (XFF) option only if the on-premises proxy is configured to add this header and your firewall blocks direct access to outbound port 443 for users who attempt to bypass the proxy.
As part of a proxy chaining configuration, you need to set the on-premises proxy server to forward all web traffic to SIA Proxy. The X-Forwarded-For (XFF) header field contains the client IP address. This value is captured in the threat events details and allows you to identify the computer that made the request. After SIA extracts the client IP address, the XFF header is removed from the request and it's not forwarded to the destination web server.
Make sure you enable XFF only if clients in your internal network use a unique IP address. If the network uses Network Address Translation (NAT), the XFF header cannot identify the client computer. For example, VMware or Windows terminal services may use unique IP addresses. In such network topologies, deploy a separate on-premises proxy behind each NAT implementation.
-
Proxy authorization. Requires that SIA Proxy authorizes connections from the on-premises proxy. SIA Proxy extracts the Proxy-Authorization header from the request and validates credentials in the header before it allows connections from the on-premises proxy. For more information on proxy authorization, see Configure proxy authorization.
For more information on setting up an on-premises proxy, see Set up on-premises proxy for SIA full web proxy.
This graphic shows the flow of traffic after proxy chaining is configured on the on-premises proxy and in the SIA policy.
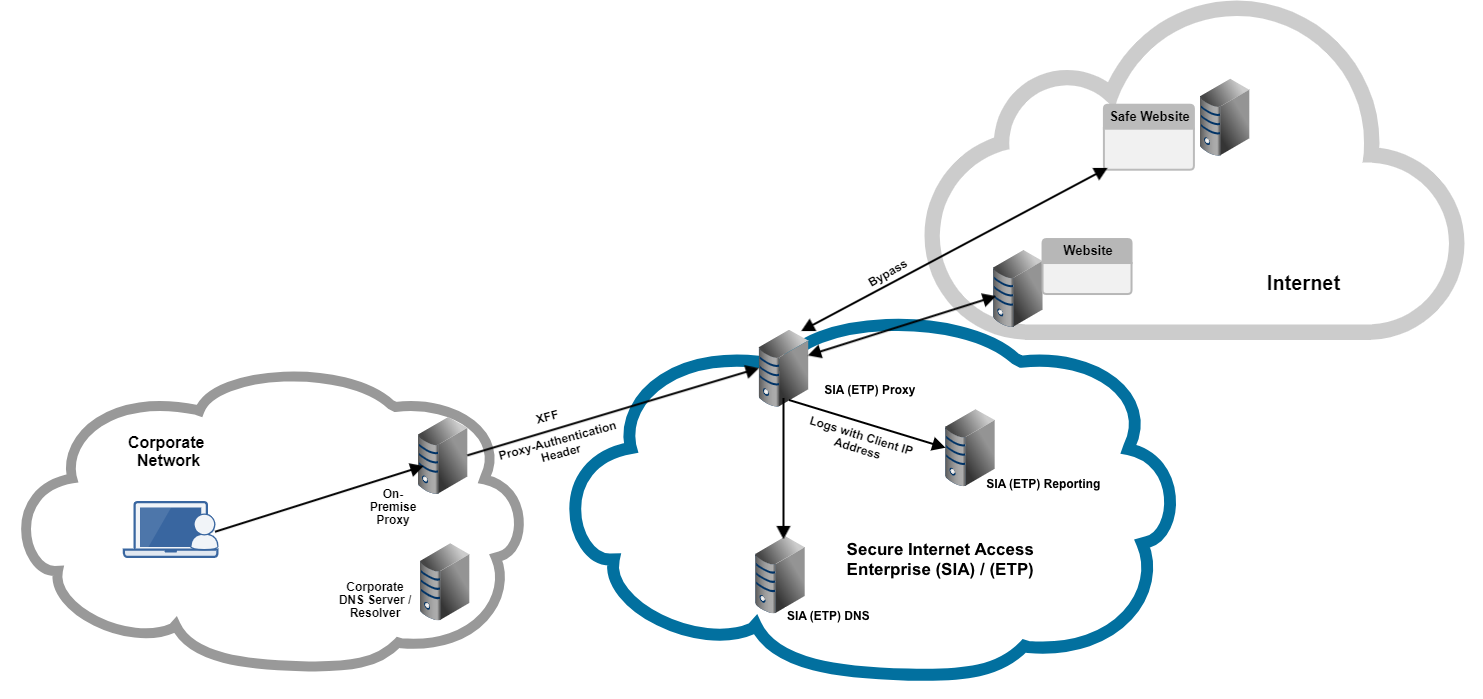
In this graphic:
-
Requests are directed to the on-premises proxy. If enabled to do so, the on-premises proxy adds the X-Forwarded-For header to identify the client IP address on the corporate network and provides a credential in the Proxy-Authorization header.
-
If proxy authorization is enabled and proxy credentials are configured, SIA Proxy authorizes connections from the on-premises proxy based on the Proxy-Authorization header. This header contains the proxy credentials that are configured in the on-premises proxy. These credentials are validated against the proxy credentials in SIA.
-
After your organization configures the on-premise proxy to forward traffic to the SIA proxy, all Internet requests are directed to SIA Proxy. If the XFF header is trusted, SIA Proxy can identify the client IP address. The client IP address is included in the reported threat events.
-
Based on the policy configuration, a policy action is applied to the traffic. If the bypass action is configured, the request bypasses TLS MITM decryption and it's sent directly to the origin IP address or the destination web server. In a policy, you define the trusted websites that do not require TLS MITM decryption and therefore, are not directed to SIA Proxy. For more information on policy actions, see Policy actions.
You can view events detected by the proxy in the Threat Events report. In the Events table, SIA includes an On-Ramp attribute that you can select to appear in the table. This attribute indicates whether traffic was directed to SIA Proxy. You can also select to show the On-Ramp Type to identify when events are detected as a result of a proxy chaining configuration. To view more details about the event, click the information icon.
Mozilla Firefox on Windows does not automatically use the proxy settings on the user's machine. After you configure proxy chaining, make sure you also configure the Firefox browser to forward requests to your on-premises proxy. For more information, see Configure Mozilla Firefox to use system proxy settings.
Updated about 4 years ago
