Application visibility and control
Application visibility and control (AVC) allows you to create a policy where you control access to web applications. You can define default policy behavior or create a policy that is based on risk level, AUP categories, category operations, applications, or specific operations for an application. You can select the users and groups that can access a web application and perform specific operations in the application.
To control the use of shadow IT and unsanctioned applications, use this feature to identify and block applications based on risk score limiting application operations.
You can use AVC with any of these SIA setups:
-
SIA DNS. If SIA Proxy is not enabled, you can still control access to applications based on the application's domain and IP address.
-
SIA Secure Web Gateway. If SIA Proxy is enabled, you can control access to applications based on URLs, domains, IP addresses, and other attributes.
A policy for AVC is divided into these components:

-
Operating Mode. You can select the mode that SIA uses for traffic by default. Unless more specific actions are defined in the policy, the behavior of these modes apply.
-
Full Proxy. Directs all web traffic to SIA Proxy, except for traffic that’s set to bypass.
-
Selective Proxy. Directs any traffic that matches a configured threat or AUP category to SIA Proxy. If no action is defined in the policy for traffic, traffic bypasses the proxy.
-
Walled Garden. Blocks all traffic unless it’s set to Allow.
If your organization uses ETP Client and has configured Walled Garden exceptions, when the client is in an unprotected state, all traffic is blocked except for the exceptions that are configured in the Local Bypass Settings. -
DNS Protection. Protects DNS traffic based on the policy. You can select this mode only when SIA Proxy is disabled.
For more information, see Default operating mode.
-
-
Mobile Mode. Defines the mode for mobile traffic when ETP Client is installed on a device. You can define the mode for these mobile devices:
- iOS. For iOS devices, you can select any of these modes: Full Proxy, Selective Proxy, and Walled Garden.
- Android. For Android devices, you can select any of these modes: Full Proxy, Selective Proxy, Walled Garden, and Proxy (Browsers Only). Proxy (Browsers Only) directs only browser traffic to the proxy.
- Chrome OS. For Chrome OS devices, you can select any of these modes: Full Proxy, Selective Proxy, and Walled Garden.
-
Risk. Defines the risk levels for a web application. Each of these levels indicate whether the application is a security risk that can result in a data breach, data loss, or other threats:
| Icon | Level | Description |
|---|---|---|
 | Critical | Indicates the application is known to be malicious and a security risk. Important: As a best practice, make sure you set the critical risk level to the block action. |
 | Very High | Indicates the application is extremely at risk for data loss or a security breach. These applications allow users to perform high-risk actions such as sending or sharing files and making remote connections that can bypass enterprise security. |
 | High | Indicates the application is moderately at risk for data loss or a security breach. These applications allow users to create and send data such as documents, multimedia content, emails, messages, voice communications, and more. |
 | Medium | Indicates the application is slightly at risk for data loss or a security breach. These applications allow users to perform slightly risky actions such as voting, rate scoring, text searches, translation, and more. |
 | Low | Indicates the application has the lowest amount of risk for data loss or a security breach. These applications allow users to perform low-risk actions such as viewing content, listening to music, downloading files, and more. |
 | Unknown | Indicates there is no application associated with the category and as a result, a risk level is not yet known for the category. |
You can click the total number of applications to view a list of applications that are associated with each risk level. You can remove a risk level from the policy configuration and assign an action to any risk level that you want to define. The actions you select in this area overrides the default action.
-
Category. Acceptable use policy and application categories that you want to assign to this policy.
You can click the total number of applications to view a list of applications that are associated with each category. You assign a policy action to a category. The action you select in this area overrides the risk level action if there is a conflict.
-
Category operations. Operations for AUP and application categories. Category operations are detected and shown in a policy if SIA Proxy is enabled for a policy.
You can click the number of associated applications to view a list of applications that support a particular operation. The configuration you set in this section only applies to applications that support the selected operation. The action you define in this area overrides the category and risk level action if there is a conflict.
-
Applications and application groups. Specific web applications as well as the operations that apply to them. Operations appear for an application as long as the application can be identified by SIA Proxy and the operation is supported by the application. If SIA Proxy is not enabled, application operations are not listed. If the application does not support an operation, it's not listed. When the proxy is not enabled, you can configure access control only for applications that SIA can identify by hostname.
To organize and help you manage your applications, you can create application groups. An application group can contain up to 50 applications. Application groups are in beta. To participate in this beta, contact your Akamai representative. For more information, see Application groups.
You can apply policy actions to the applications and application operations in a group, as well as to the individual applications or application operations that are assigned to a policy.
The action or actions you select in the applications area override the category operations if there is a conflict.
As you define each level in this policy, the detailed levels you configure take precedence over more general settings. For example, the policy action you apply to an application takes precedence over an action that's applied to its corresponding category or category operation.
This illustration shows the priority of these components in a policy. The operating mode is shown as a more general setting with the least priority as administrators define other levels of the policy. However, the operating mode applies if there is no configuration in place elsewhere in the policy for traffic.
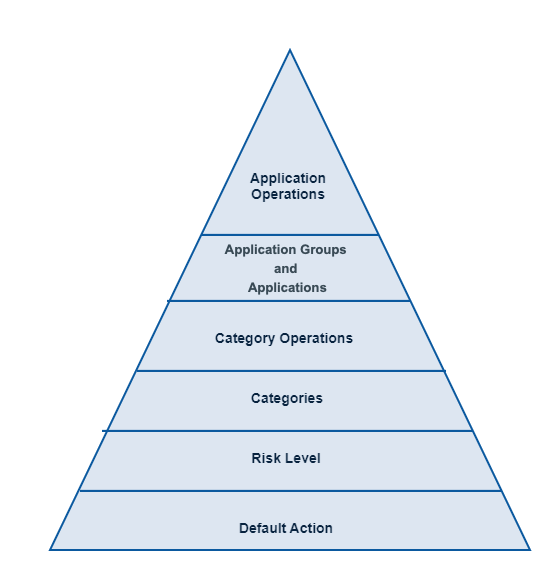
Consider these examples:
-
If you define a block action to a high risk level and you select an allow action for a high risk category such as Sales and Marketing, web applications in this category are still allowed. The risk level setting still applies for other traffic that's not specifically defined at the category level of the policy.
-
If you select the block action to a File Transfer (Collaboration and Online Meetings) category operation and allow the file transfer operation in a specific application such as Slack, the allow action for transferring files to Slack takes precedence over the block action in the category operation.
SIA may update the list of applications, application operations, and categories in a policy. If an application, operation, or category is discontinued, a message appears to notify administrators about this update. After an administrator confirms the message, SIA removes the unsupported settings from the policy. Administrators need to then redeploy the policy. For more information, see Updated list of access control applications.
Policy actions
Depending on the component that you are configuring in the policy for AVC, these actions may be available:
-
Bypass. Traffic bypasses SIA Proxy and is directed to the origin.
-
Allow. Traffic is directed to SIA Proxy where it's analyzed and assigned a category. Based on the category, a policy action is applied. If the proxy is disabled, traffic is directed to the origin.
-
Monitor. Traffic is allowed and an event is logged.
-
Block. Traffic is blocked and users are shown an error page. The following applies:
-
If the proxy is not enabled in a policy, you can select to show an error page or have traffic directed to a custom response. This option is available for risk levels, categories, category operations, applications, and application operations. For more information about custom responses, see Configure a custom response.
-
If there are operations supported for a selected application, the application operations also appear. By default, they are assigned the same action as the application. Depending on the action of the application, you may or may not be able to modify the action of the application operation:
- If you select the block action, you cannot modify the action of the application operation.
- If you select an action that is not block (for example, monitor, bypass, or allow), you can modify the action of the application operation.
-
Note that not all these actions are available in each area of the policy for AVC. Also, for some applications, the bypass action may not be available. This occurs if the application cannot be identified by domain and is only detected by SIA Proxy through a URL.
Exceptions to a block action
If you select the block action in the risk, category, category operations, and applications area, you can define any user or group that are exceptions to the block action.
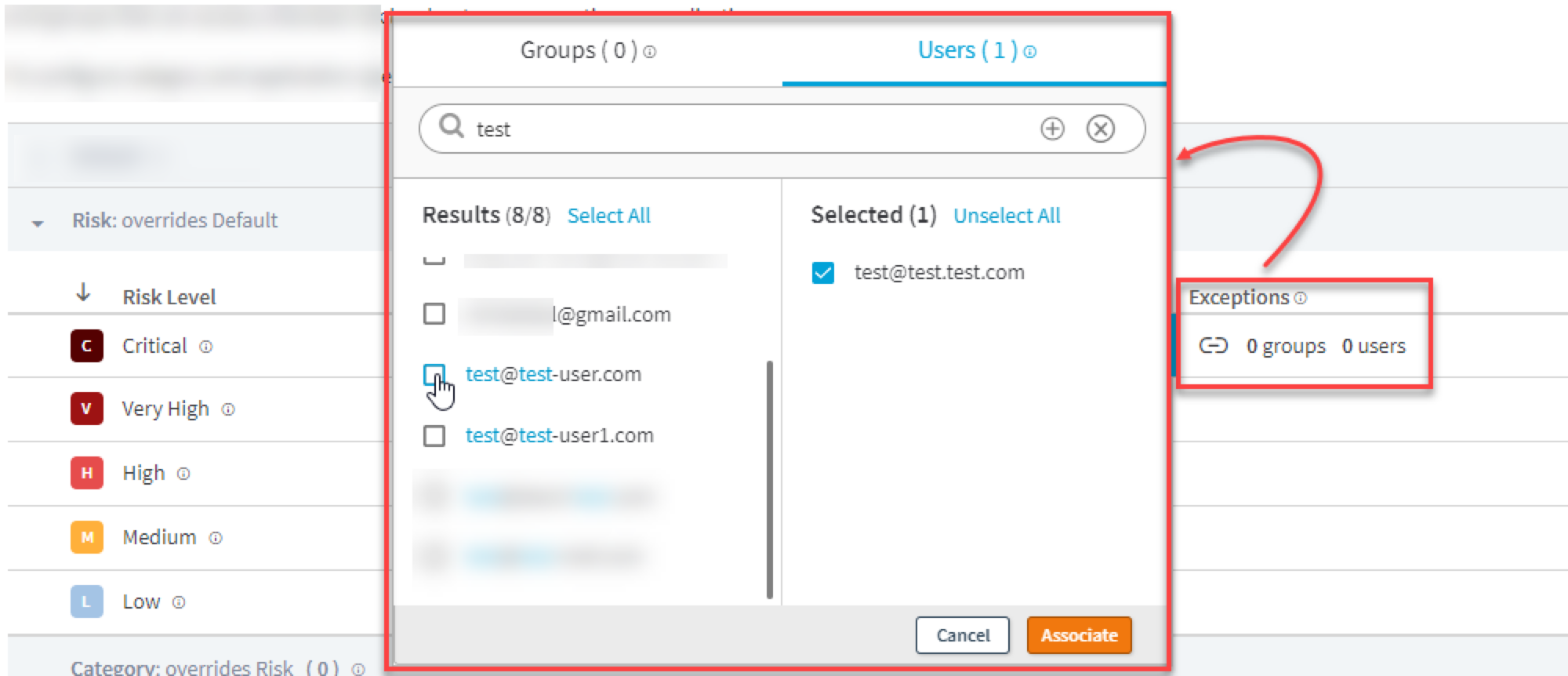
You can select users and groups when this policy configuration is in place:
-
An Optional or Required authentication mode is set in the policy. For more information, see Authentication policy.
-
An identity provider is associated with the policy. As part of an IdP configuration, you'll associate the directory that contains users and groups. For more information, see About identity providers.
With this configuration, the selected users and groups can access the content you block.
For application and application operations, you can additionally define device posture risk levels. Device posture allows you to set the requirements that desktop and mobile devices must meet to access an application or complete an application operation. You define risk levels in Enterprise Application Access for the low and medium tiers. All devices that do not meet the criteria for these tiers are considered a high risk and are automatically blocked.
For AVC, you can select from these risk levels:
- Low Only. Provides access to devices that meet requirements in the low tier.
- Low & Medium. Provides access to devices that meet requirements for the low or medium tiers.
Note the following:
- Selected users and groups can access an application or application operation if their device meets the tier requirements that are defined for the selected risk level.
- If no user or group is selected as an exception for an application or application operation, all users with devices that meet the device risk level requirements are granted access.
For more information on device posture, see Use device posture for application access.
Analytics
SIA shows AVC data in these reports:
-
Access Control. Contains events for violations to AVC, DLP, and blocked file types. For AVC, you can filter events based on category, risk level, operation, and application.
-
DNS Activity. Contains data on DNS traffic. For AVC, you can filter activity by category, risk level, and application.
-
Proxy Activity. Contains data on SIA Proxy traffic. For AVC, you can filter activity by risk level, operation, and application.
SIA also offers dashboard widgets that generate information specific to AVC. To track risky applications, machines, and users, administrators can add these widgets to their Enterprise Center dashboards:
- Top Risky Applications
- Top Risky Machines
- Top Risky Users
For more information about the dashboard, see Dashboard.
Application groups
In a policy, you can organize applications into logical groups that help you manage them. For example, you may want to organize applications based on application type or based on the policy action you want to apply.
Application groups are in beta. To participate in this beta, contact your Akamai representative.
You can create application groups as you assign applications to a policy. Consider the following:
- An application group can contain up to 50 applications.
- If an application group is selected in a policy, you cannot select the applications in that group as separate applications for the policy. Similarly, in a policy, you cannot select applications that are part of an application group.
- In a policy, you cannot select application groups that share one or more applications.
- After you create an application group, make sure you associate it to the policy.
- You can associate an application group to multiple policies.
- You assign policy actions to individual applications and application operations in a group.
Configure application visibility and control
Application visibility and control allows you to control access to web applications. In this procedure, you'll define different components. This includes risk level, categories, category operations, applications, and application operations. The specific settings you define in the policy are prioritized over more general settings. For more information, see Application visibility and control.
To configure AVC:
-
In the Threat Protection menu of Enterprise Center, select Policies > Policies.
-
Click the name of the policy that you want to edit.
-
Go to the Settings tab.
-
For the Policy Type menu, make sure DNS + Proxy is selected as the policy type. While the proxy is not required for configuring AVC, you cannot configure category operations without enabling it.
-
If you enabled the proxy, make sure inline payload analysis is also enabled.
-
If you want to configure user and group exceptions to any blocked content in an AVC policy:
-
Make sure Required or Optional is selected as an Authentication Mode. For more information, see Authentication policy.
-
In the IdP menu, select an identity provider if one is not selected.

-
-
Click the Access Control tab.
-
Click the AUP & Shadow IT subtab.
-
Expand the Operating Mode area and select a mode, as shown in this example.

These modes are available:
-
Selective Proxy. Directs any traffic that matches a configured threat or AUP category to SIA Proxy. If no action is defined in the policy for traffic, it bypasses the proxy.
-
Full Web Proxy. Directs web traffic to SIA Proxy, except for traffic that’s set to bypass.
-
Walled Garden. Blocks all traffic unless it is set to Allow.
If your organization uses ETP Client and has configured Walled Garden exceptions, when the client is in an unprotected state, all traffic is blocked except for the exceptions that are configured in the SIA network configuration.
-
DNS Protection. Protects DNS traffic based on policy. You can select this mode only when SIA Proxy is disabled.
-
-
Expand the Mobile Mode area and select a mode based on the device operating system.
-
Selective Proxy. Directs any traffic that matches a configured threat or AUP category to SIA Proxy. If no action is defined in the policy for traffic, it bypasses the proxy. This is the default mode for mobile devices.
-
Full Proxy. Directs web traffic to SIA Proxy, except for traffic that’s set to bypass. This mode is recommended for managed devices. Make sure you test your managed applications and bypass any applications that fail.
-
Walled Garden. Blocks all traffic unless it is set to Allow.
-
Proxy (Browser Only). Directs only browser traffic from an Android device to the proxy. Application traffic is directed to the origin. This mode is available for Android devices only.
-
-
Expand the Risk area and select a policy action for any of the risk levels that you want to define in the policy. In the Action column heading, you can select an action for all risk levels, or you can select an action for an individual risk level. To remove a risk level, click the minus icon. As a best practice, select the block action for the critical risk level. If you select a block action and an IdP is selected on the Settings tab, complete these steps to assign a user or group exception:
-
Click the link icon in the exceptions column. A window appears.
-
In the Groups tab, search for a group and select the group or groups that you want to exempt from the block action.
If the group name you provide does not appear in the drop-down list, you can add the group. If you add a group, you need to also add the group to the relevant directory for the group to authenticate and gain access.
-
In the Users tab, search for the users and select the users that you want to exempt from the block action.
If the user does not exist in the directory associated with the policy IdP, you can enter a unique ID for a user you want to add and click the add button. This adds the unique ID to the list. You need to also add the user to the relevant directory for the user to authenticate and gain access.
The user ID provided in this example is the ID the user enters to authenticate:

-
Click Associate.
-
-
Expand the Category area and consider the policy actions you want to apply to a category or categories, for example, you may choose to block Gambling websites:
- Click the link icon and select the categories that you want to associate with the policy. Click Associate.
You can select a policy action as you associate a selected category or after you associate a category.
-
Select an action for each category. In the action column, you can select an action for all categories, or you can select an action for an individual category.
-
If you select a block action and an IdP is selected on the Settings tab, complete steps 11a to 11d to assign a user or group exception.
-
Expand the Category Operations area and consider the policy actions that you want to apply to an operation or operations, for example, you can search for all upload operations, select these operations for your policy, and select to block them across all categories:
- Click the link icon and select the category operations that you want to associate to the policy. Click Associate.
You can select a policy action as you associate a category operation or after you associate a category operation.
-
Select an action for each category operation. In the action column, you can select an action for all category operations, or you can select an action for an individual category operation.
-
If you select a block action and an IdP is selected on the Settings tab, complete steps 11a to 11d to assign a user or group exception.
-
Expand the Applications and Application Groups area and consider the policy actions that you want to apply to applications:
-
Click the link icon and select applications and application groups that you want to associate to the policy. Click Associate. To create an application group, see Create an application group.
Application groups are currently in beta. To participate in the beta, contact your Akamai representative.
-
Select an action for each application. If you associated an application group, you can expand the group to view its applications. You can then select an action for each application in the group.
If there are operations supported for a selected application, expand the application to view the operations. By default, they are assigned the same action as the application. Depending on the action of the application, you may or may not be able to modify the action of the application operation:
- If you select the block action, you cannot modify the action of the application operation.
- If you select an action that is not block (for example, monitor, bypass, or allow), you can modify the action of the application operation.
-
If you select a block action and an IdP is selected in the Settings tab, you can configure exceptions to the block action:
-
To assign users or groups exception, complete steps 11a to 11d.
-
To require that desktop and mobile devices meet specific risk level requirements, select a risk level. You can select Low Only or Low & Medium. Low Only indicates that devices must be a low risk, while Low & Medium indicates that devices can be a low risk or a medium risk.
Your organization must be licensed for Enterprise Application Access (EAA) to use this feature. The risk levels you select are defined in EAA as part of the setup for device posture. For more information, see Use device posture for application access.
-
-
-
Click Save. If you want to save and deploy the policy, click Save and Deploy.
Next steps
If you haven’t deployed the policy, make sure you deploy it to the SIA network. For instructions, see Deploy configuration changes.
Create an application group
As you select applications for a policy, you can create an application group. An application group allows you to more easily manage the applications that you assign to a policy. You can assign an application group to multiple policies. An application group can contain up to 50 applications.
Application groups are in beta. To participate in the beta, contact your Akamai representative.
To create an application group:
- Create a policy and configure application visibility settings in the AUP & Shadow IT tab of the policy. For instructions, see Configure application visibility and control.
- In the Applications and Applications Groups section of the AUP & Shadow IT tab, click the link icon.
- Click the plus sign icon to create an application group.
- Enter a group name.
- Click the link icon to select applications and select Associate.
- Click Save.
Next steps:
Assign the application group to the policy. In the Application and Applications area, make sure you are in the window where you can select applications or applications groups. Select the application group and click Associate. Click Save or Save and Deploy for the policy. For more information on configuring a policy for AVC, see Configure application visibility and control.
Manage application groups
After you create an application group, you can remove or add applications from the group as needed. If the application group you modify is assigned to a policy, the update automatically affects the policy.
Application groups are in beta. To participate in the beta, contact your Akamai representative.
To manage application groups:
- In the Applications and Application Groups section of the AUP & Shadow IT policy tab, click the link icon.
- In the Application Groups area, click the gear icon. The Manage Application Groups window appears.
- Click the edit icon of the Group to modify the group. You can change the group name or click the link icon to add or remove applications. After making your changes, click Save.
- To remove a group, click the trash bin.
- Click Cancel or exit the window to return to the policy configuration.
Default operating mode
With the Operating Mode setting, you define how SIA handles traffic by default unless you configure more specific actions for lists, threat categories, and for AUP or AVC settings. These modes are available:
-
Full Proxy. Directs all web traffic to SIA Proxy, except for traffic that’s set to bypass.
-
Selective Proxy. Directs domains and risky web traffic to SIA Proxy for threat inspection. This includes traffic that matches a configured threat or AUP category.
-
Walled Garden. Blocks all traffic unless it’s configured with the Allow action.
If your organization uses ETP Client and has configured Walled Garden exceptions, when the client is in an unprotected state, all traffic is blocked except for the exceptions that are configured in the Local Bypass Settings.
-
DNS Protection. Protects DNS traffic based on policy. You can select this mode only when SIA Proxy is disabled.
For information on configuring the default action as part of AVC, see Application visibility and control and Configure application visibility and control.
You can also configure a mode for your mobile devices. This is a setting that’s also set in the policy as part of AUP and AVC. For more information, see Mode for mobile devices.
Depending on your organization's requirements and the balance your organization needs to maintain between security, privacy, and user productivity, you can configure SIA policy and the operating mode based on one of these scenarios:
-
Scenario 1: Balance security and user productivity (Recommended). If you want to block known threats and scan all other traffic, consider this configuration:
-
Enable SIA Proxy as a full web proxy.
-
Select Full Web Proxy as the Operating Mode.
-
Block all known threats. You can choose the block action for threat categories and for specific custom lists that contain known threats.
For instructions, see Enable full web proxy.
-
-
Scenario 2: Allow only known, trusted traffic (walled garden). If you want to block most traffic and grant users access to known, safe websites only, consider this configuration:
-
Create an exception list that contains the websites that you want users to access.
-
Select Walled Garden as the Operating Mode.
-
Block all threat categories.
-
Mode for mobile devices
When ETP Client is installed on a mobile device, you can define how mobile traffic is handled. Similar to the operating mode that’s used for general traffic, you can select a specific proxy type or configure a walled garden.
You need to enable and set up SIA Proxy to configure mobile mode settings in a policy.
This table lists the mobile devices that are supported and the modes that are available for these devices:
| Mobile Operating System | Available Modes |
|---|---|
| iOS (includes iPadOS) |
|
| Android |
|
| Chrome OS |
|
You can select from these modes:
-
Selective Proxy. Directs any traffic that matches a configured threat or AUP category to SIA Proxy. This is the default mode for mobile devices.
-
Full Proxy. Directs all web traffic to the proxy, unless traffic is configured for bypass in the policy. This mode is recommended for managed devices. Make sure you test your managed applications and bypass any applications that fail.
-
Walled Garden. Blocks all traffic unless it’s set to Allow in the policy.
-
Proxy (Browser). This mode is available for Android devices only. It directs only browser traffic to the proxy. Application traffic is directed to the origin and not scanned by the proxy.
For more information about the operating mode, see Default operating mode.
Walled garden
A walled garden blocks all traffic except for the traffic that’s explicitly allowed in the policy. You can define a walled garden as an operating mode in SIA policy. This is the default mode that’s applied to traffic unless more detailed settings are configured in the policy. If the proxy is enabled, you can also set walled garden as the mode for your mobile devices. You can select walled garden as a mode for iOS, Android, and Chrome OS devices. For more information, see Default operating mode and Mode for mobile devices.
Allowed traffic in a walled garden includes:
- The domains, IP addresses, URLs, and file hashes that you define in an exception list.
- Any risk level, category, operation, and application that you set with the Allow action under Access Control.
- Any traffic that's configured in the Local Bypass Settings.
When traffic is blocked with a walled garden, users are presented with an SIA error page to indicate that the website is blocked and prohibited. For more on SIA error pages, see Customize error pages.
Note the following when configuring a walled garden:
- If the mobile mode is set to Walled Garden for any mobile device, make sure you also select Walled Garden as the default operating mode in the policy.
- If you select the full proxy for any mobile device or you select Proxy (Browser Only) mode for Android, make sure the default operating mode is not set to Walled Garden.
Configure a walled garden
Before you begin:
- Make sure the Local Bypass Settings contain the internal traffic that you want users to access. For more information, see Configure local bypass settings.
- Make sure you create exception lists with the traffic that you want to allow. For more information, see Exception lists.
You can configure a walled garden to block all traffic except for the traffic that your organization wants to allow.
To configure a walled garden:
-
In the Threat Protection menu of Enterprise Center, select Policies > Policies.
-
Click the name of the policy that you want to edit or click the edit icon that appears when you hover over the policy.
-
Click the Access Control tab.
-
Click the AUP & Shadow IT subtab.
-
For the Operating Mode, select Walled Garden.
-
Under Mobile Mode, select Walled Garden for iOS, Android, and Chrome OS devices.
-
To add an exception list, see Add an Exception list to a policy.
-
Click Save. If you want to save and deploy the policy, click Save and Deploy.
Next Steps
If you haven’t deployed the policy, make sure you deploy it to the SIA network. For instructions see Deploy configuration changes.
Application visibility and control categories
These categories are available when you configure AVC in a policy. For more information on AUP categories, see Acceptable use policy categories.
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Collaboration and Online Meetings | Cloud applications that offer online communication and collaboration services such as online meetings, Internet telephony, messaging, voice over IP (VoIP), and more. |
| IT Services | Cloud applications that offer IT services, such as device and identity management. |
| Productivity and CRM Tools | Cloud applications that offer productivity and management tools. This includes customer relationship management (CRM) tools. |
| Sales and Marketing | Cloud applications that offer sales and marketing tools. |
| System and Development | Cloud applications that offer system and development tools. |
| Internet Utilities | Cloud applications that offer general Internet services and utilities. |
| Document Management | Cloud applications that secure document information, such as data in an electronic form. |
Updated list of access control applications
Policy settings that are defined for applications, categories, and operations may require removal based on updates from the intelligence feeds. When you open a policy that requires this kind of update, SIA displays the settings that need to be removed, as shown in this example:
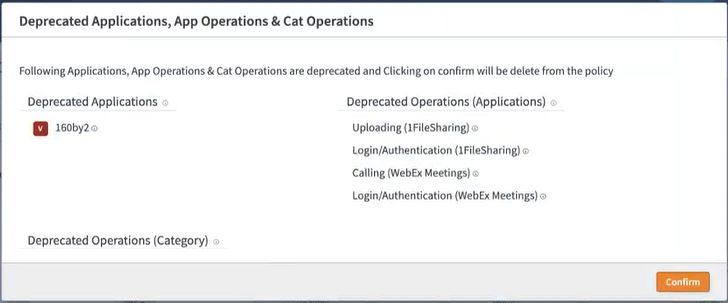
To remove the unsupported policy settings, click Confirm and deploy your changes.
Updated 7 months ago
