ETP Client for web traffic
With ETP Client, you can:
-
Direct all web traffic to SIA Proxy and scan it for malware. The client supports users who are on or off the corporate network.
-
Provide SSO to all applications on the client computer after a user authenticates to access websites or applications on the web. This configuration is based on SIA policy and IdP settings. ETP Client also authenticates devices to SIA Proxy. As a result, HTTP traffic from a specific device is tied to the user’s identity. For more information, see Authentication policy.
-
Split traffic to ensure that users can directly access websites on the local network and these requests are not forwarded to SIA Proxy.
-
If an exception list with a bypass action is configured in a policy or you configured local bypass settings, ETP Client directs this traffic to its destination. Akamai also maintains a list of traffic that’s not directed to SIA Proxy for compliance and performance reasons. For more information, see Bypass list.
-
Enable walled garden. You can use ETP Client to block all traffic when it’s in an unprotected state. This setting blocks all traffic except for the domains and IP addresses that are configured as exceptions in the Local Bypass Settings. This feature is enabled in the policy and applies to the desktop client. For more information on configuring walled garden exceptions, see Configure walled garden exceptions.
-
Support multiple users on the same device. Version 4.4.0 on Windows provides additional support when multiple users share the same device. For example, you can use ETP Client on a device that’s set up as a kiosk. After a new user accesses the device, there may be a short period of time where ETP Client has not yet synchronized with the identity provider to identify the user and grant access. Version 4.4.0 offers login and logout buttons. This allows the previous user to log out and the new user to log in. A user enters Login Portal credentials to access the network resources you’ve permitted through the identity provider and the SIA policy configuration. To enable this feature, contact your Akamai representative.
As part of the setup for ETP Client, you enable the proxy and perform the setup that’s required for the proxy such as generating or uploading the MITM certificate in SIA for TLS decryption. For more information, see Set up SIA Proxy.
To forward all web traffic to ETP Client, you can configure ETP Client as a local web proxy on the user’s machine or you can configure it as a transparent proxy that intercepts traffic.
Local web proxy
From a policy or in the ETP Client configuration settings, you can configure ETP Client as the local web proxy on the user’s device. When one of these settings is enabled, ETP Client modifies the local proxy settings on the user’s device to make it the proxy. This allows the client to forward all traffic to SIA Proxy.
In a policy, this setting is called Overwrite Device Proxy Settings. It modifies the local web proxy when Yes is selected. It also modifies the proxy settings when there’s no local proxy configured and the Only if there’s no local proxy option is selected. This setting applies to all clients that are associated with the policy. It also takes precedence over the client configuration setting.
In the ETP Client configuration, an administrator can select the Configure ETP Client as local computer web proxy setting and further modify the proxy port if needed. By default, ETP Client listens for traffic on port 8080. If this port is used by another process in your network, you can enter a new port into this field.
If you selected Yes to Overwrite Device Proxy Settings or Configure ETP Client as a local computer web proxy and then decide to disable the setting by selecting No, ETP Client does not save and restore the previous proxy settings that were on the device. These settings will also overwrite any PAC file configuration that's set in the browser or device.
Transparent traffic interception
In the configuration of ETP Client and the Threat Protection service of Zero Trust Client, you can enable the Transparent Traffic Interception setting to have the client intercept and capture traffic without modifying browser or operating system settings. This allows the client to act as a transparent proxy.
On Windows, Zero Trust Client and ETP Client 4.1 or later automatically installs a driver that allows the client to securely capture traffic. The client then forwards DNS traffic to SIA resolvers and web traffic to SIA Proxy. It's currently supported on Windows 11 and Windows 10.
On macOS, ETP Client 4.3 or later uses the Apple Network Extension framework to intercept traffic. As you install or upgrade the client, you must allow ETP Client Extensions to use the client and intercept traffic. While administrators are prompted to enable the client extensions after installation, you can enable them at any time in the Security & Privacy system preferences. The extensions are required to use ETP Client 4.3 or later of the client.
This feature is currently in beta on macOS.
If the client was previously set to modify the local web proxy settings, enabling transparent traffic interception will revert the local web proxy to its previous state where no local web proxy is configured.
When using the client with transparent traffic interception, note the following:
-
If your organization uses Enterprise Application Access (EAA) Client, make sure you add the destination IP address or CIDRs of any client-based application that you don’t want scanned by the proxy to the Local Bypass Settings. By default, the internal IP addresses that are part of RFC 1918 and RFC 4193 are added to the Local Bypass Settings.
-
Browser sessions that were open while the client was in an unprotected state will remain open even if the client returns to a protected state.
-
If there is a system crash on a Windows machine (blue screen error), ETP Client disables itself for three minutes.
-
If a Windows machine is already using an Npcap version that is earlier than 0.9988, ETP Client is not able to redirect traffic. This occurs as a result of a known issue in Npcap. In this situation, ETP Client disables itself on the machine.
-
You can specify Windows applications that have traffic you don’t want directed to ETP Client or Zero Trust Client. For more information, see Configure local bypass settings.
-
You can specify the hardware IDs of network interfaces that have traffic you don’t want directed to Zero Trust Client. For more information, see Configure local bypass settings.
Additional requirements for ETP Client
To use ETP Client in your network, make sure these conditions apply:
-
ETP Client locations on the corporate network are configured in SIA. This includes public IP addresses of all exit points or gateways in the corporate network. These addresses allow SIA to identify the location where traffic is coming from and apply the policy that corresponds to this location.
-
When ETP Client is off the corporate network and connects from an IP address that is not configured as a location in SIA, the policy for the Off Network Client setting is applied. Similarly, if a user is visiting a network, ETP Client applies the policy of the user’s corporate network. It does not apply the policy of the visiting network. In this case, the policy associated with the Off Network Client setting in the user’s corporate network takes effect.
-
Configure the DNS suffixes and IPv4 and IPv6 addresses ranges of internal corporate network resources and websites. This is done in the Local Bypass Settings. ETP Client directs traffic to these websites to their destination and in turn, bypasses SIA Proxy. If your organization also uses Enterprise Application Access (EAA), you can provide the hostnames of EAA applications.
Similarly, you can create an exception list with the domains and IP addresses that you prefer bypass SIA Proxy. You can then assign this list to an SIA policy. For more information, see Add a custom exception list.
-
On Windows machines where ETP Client will be installed, make sure Web Proxy Auto-Discovery (WPAD) for WinHTTP is running. For more information, see Web Proxy Auto-Discovery (WPAD) on Windows.
-
Harden devices in your network to prevent users from changing proxy settings.
-
Do not enable authentication on client devices that are shared by more than one user. Keep in mind that after a user authenticates on a client device, ETP Client grants SSO to applications and websites based on that user’s identity.
-
Enable SIA Proxy in the policy associated with the Off Network Client setting.
-
In addition to installing ETP Client on user computers, laptops, and supported mobile devices, you can also install it on server machines.
-
If there is another proxy deployed between ETP Client and the on-premises proxy, make sure you don't configure this proxy with the TLS MITM certificate. Avoiding this improves performance.
The default settings on Mozilla Firefox and Microsoft Edge browsers may not support ETP Client:
Mozilla Firefox does not automatically use the proxy settings on the user's device. If you configure ETP Client as a local web proxy or you set up proxy chaining, you need to configure Firefox to use the system proxy settings. For more information, see Configure Mozilla Firefox to use system proxy settings.
By default, Microsoft does not allow Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps such as Microsoft Edge to communicate with a network server that's listening on the localhost. When the proxy is enabled, communication with the localhost is necessary. To allow the use of Edge when SIA Proxy is enabled, see Allow ETP Client connections on Microsoft Edge.
Network flow
These graphics show how ETP Client behaves when the forward proxy setting is enabled in a policy. These graphics illustrate the network flow when there’s no on-premises proxy and when there's an on-premises proxy.
ETP Client in a network without on-premises proxy
In this scenario, ETP Client is configured as the local web proxy on the device where the client is installed or it’s configured for transparent traffic interception:
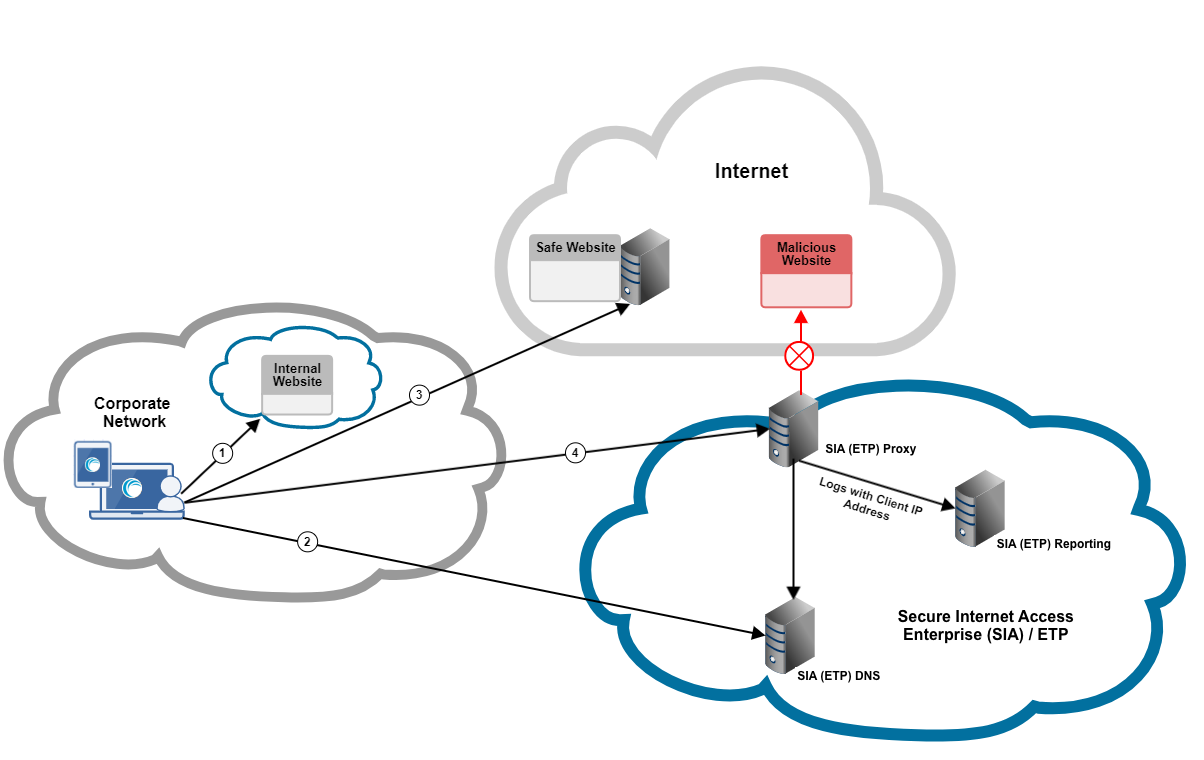
In this graphic:
-
Traffic to local websites is split from remote traffic. Based on the Local Bypass Settings in SIA, requests to internal websites go directly to their destination.
-
ETP Client checks whether some remote websites should bypass the proxy.
-
ETP Client directs web traffic that’s configured to bypass SIA Proxy to its destination. These domains and IP addresses were configured in an exception list and assigned to a policy with the bypass policy action.
-
Web traffic that is not specifically defined in an exception list or in the Local Bypass Settings is directed to SIA Proxy for analysis.
ETP Client in a network with an existing on-premises proxy
In this scenario, ETP Client is not configured as the local web proxy on the device where the client is installed. This occurs when the Configure ETP Client as local computer web proxy setting is set to None or to the Only if there’s no local proxy option when there’s an existing proxy. Transparent traffic interception is also not enabled.
Depending on whether the on-premises proxy forwards traffic to SIA Proxy, ETP Client shows a protected or not protected status as shown in this graphic:
Protected by local network
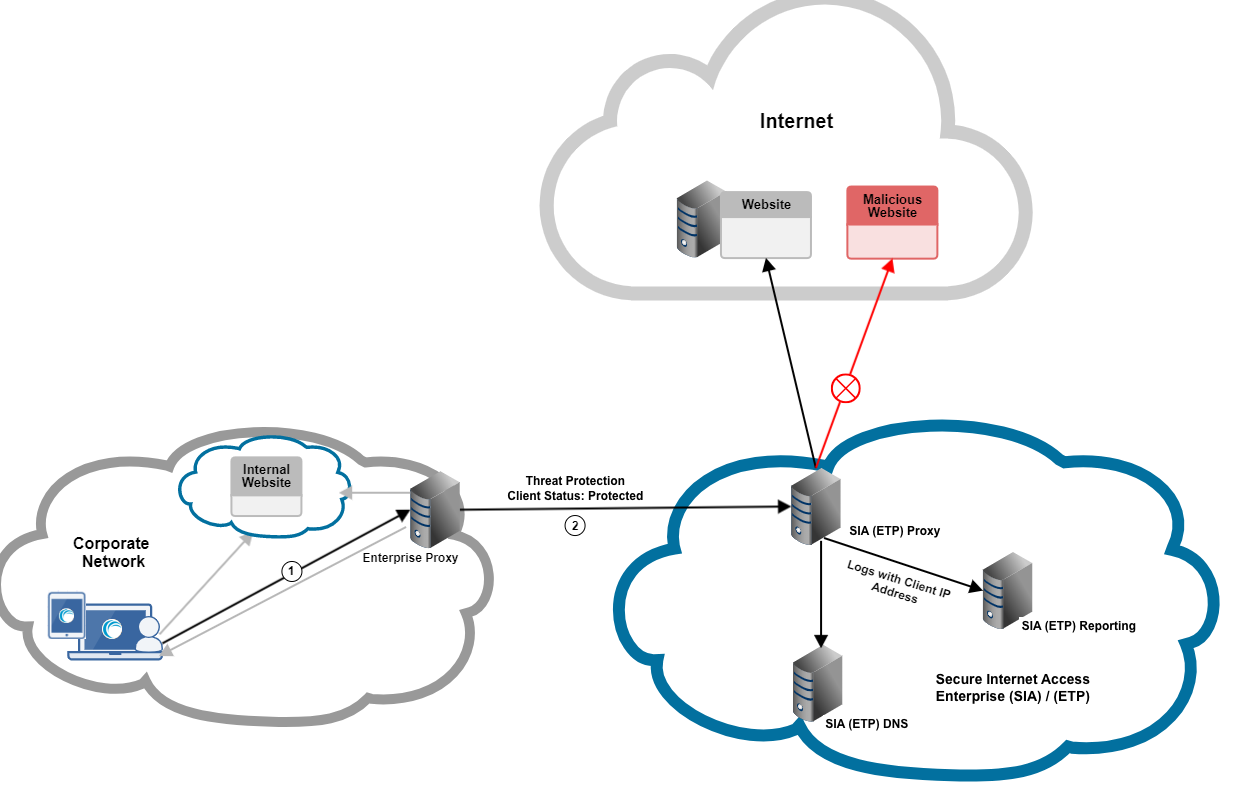
This flow applies:
- ETP Client sends requests to the enterprise proxy. ETP Client allows the enterprise proxy to decide whether requests to internal websites or resources are handled by the enterprise proxy or by ETP Client.
- In this scenario, ETP Client does not overwrite local web proxy settings. As a result, ETP Client probes the enterprise proxy to determine what status to show. The protected status appears because proxy chaining is configured and the enterprise proxy forwards traffic to SIA Proxy.
Not Protected
In this situation, while ETP Client forwards requests to enterprise proxy, it shows your device is NOT protected or unprotected status because the enterprise proxy does not forward the request to SIA Proxy:
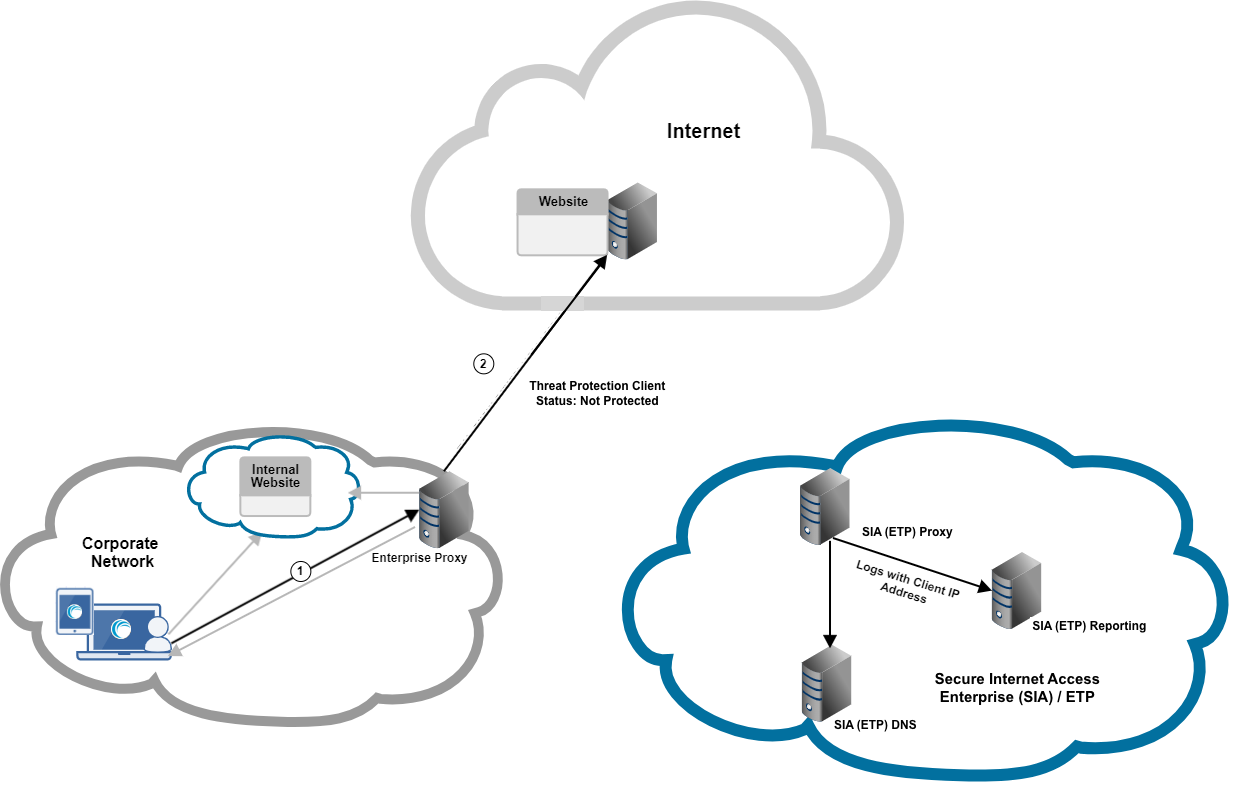
When ETP Client is not configured to overwrite local web proxy settings or transparent traffic interception is not enabled, the client probes SIA Proxy to determine what status to show. The status indicates the user’s device is not protected because proxy chaining is not set up.
For more information on the statuses, see ETP Client on desktop computers and machines.
Updated about 2 years ago
