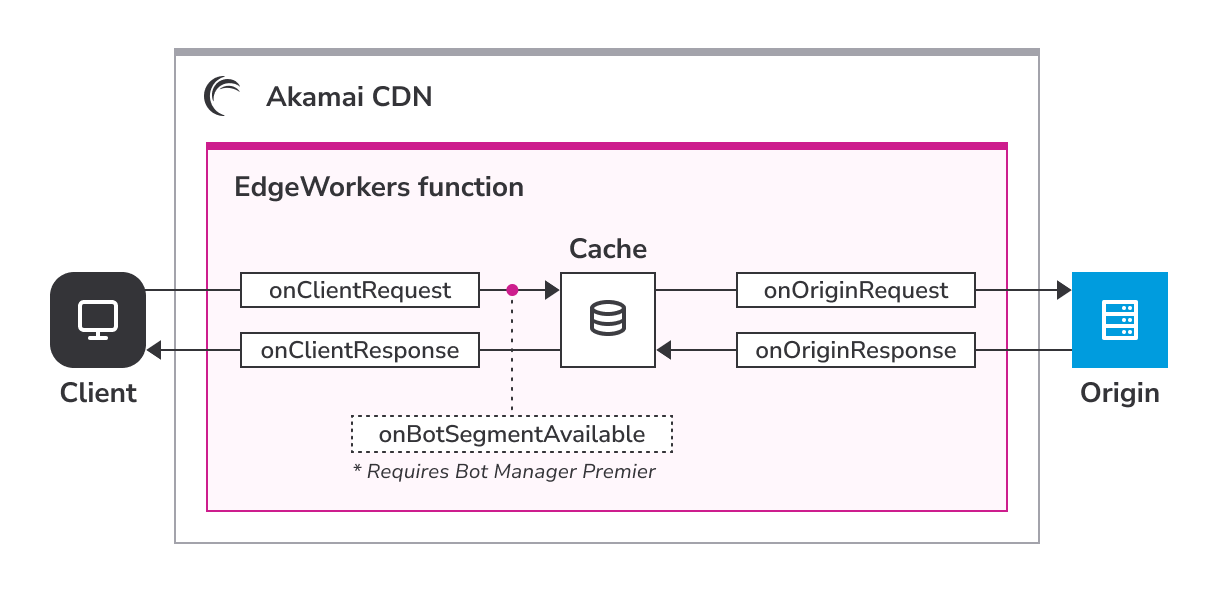
EdgeWorkers event model
Understand when EdgeWorker scripts are executed. The EdgeWorkers code is invoked based on specific HTTP events. To create a function for any of these events, implement the callbacks as explained in the JavaScript API reference.
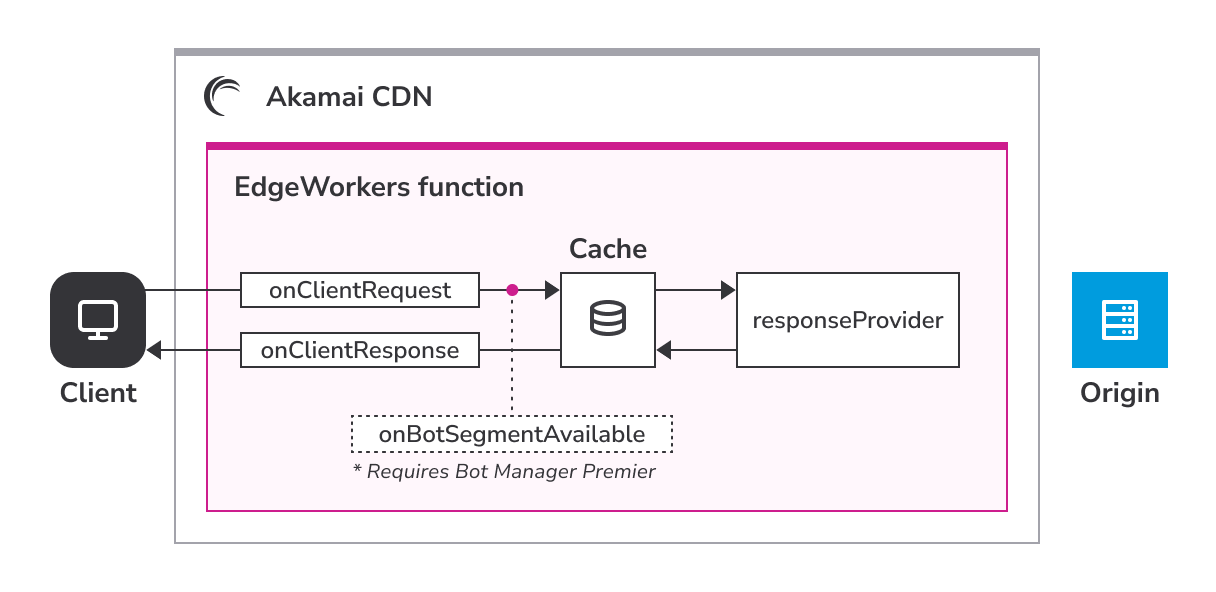
The responseProvider event handler acts as a surrogate origin to execute EdgeWorkers code. To learn more, go to the Response Orchestration section.
onClientRequest
The onClientRequest event happens for every request as the request is received, before checking if a response is available in cache. Use this event for request modifications before going to cache or to origin. Here's an example of a function that modifies the response based on user location:
// redirect based on originating country of request
export function onClientRequest(request) {
var country = request.userLocation.country;
if (country === 'FR') {
request.respondWith(302, {'Location': ['https://www.example.com/fr/']}, '');
}
}
Review the table for information about the available parameters.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| request | Request | An object representing the current request. Modifications to this request object are visible in all other event handlers. |
onBotSegmentAvailable
If your property has been configured to use Bot Manager Premier, then the onBotSegmentAvailable event happens after onClientRequest and before checking if a response is available in cache. Use this event to inspect the bot score assigned to the request by Bot Manager.
Any headers that you add to the onClientRequestrequest are not guaranteed to be visible in the onBotSegmentAvailable event handler, they are visible in event handlers on later stages of the request processing. Furthermore, the addHeader, setHeader, removeHeader APIs on the request object API and CacheKey objects manipulation API are not available in onBotSegmentAvailable.
Here's an example of a function that modifies the response based on the bot score.
//redirect base on botScore
export function onBotSegmentAvailable(request) {
if request.botScore.responseSegment.isStrictResponse() {
request.respondWith(302, {'Location': ['https://example.com/challenge']}, '');
}
}
Review the table for information about the available parameters.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| request | Request | An object representing the current request. Modifications from the onClientRequest event may not be visible. |
Interactions with Bot Manager actions
- If Bot Manager activates a deny action, the
onBotSegmentAvailableevent will not run. A property may set the PMUSER_EXECUTE_EW_ON_WAF_DENY metadata variable to run the event on deny actions. onBotSegmentAvailablewill only run once per request regardless of the metadata stage order. If Bot Manager activates a serve-alternate action and an EdgeWorker is configured on the alternate domain, then theonBotSegmentAvailablewill not run a second time if it already ran for the original domain. If the serve-alternate action was executed beforeonBotSegmentAvailable, then onBotSegmentAvailable may still run on the alternate domain.- When processing a request results in a new request, for example, a sub-request to a domain with subWorkers enabled, then
onBotSegmentAvailablemay run on the second request.
onOriginRequest
The onOriginRequest event happens just before sending the request to the origin. This event only happens if the response is not served from cache and not constructed on the edge. Use this event if you want to affect the response coming back from the origin. Changes to the Request Object made during onOriginRequest update the outgoing request to the origin. The changes are not visible in later event handlers.
This function adds a device type header to the origin request:
// send header to origin
export function onOriginRequest(request) {
if (request.device.isMobile) {
request.setHeader('X-MyHeader-DeviceType','Mobile');
}
else if (request.device.isTablet) {
request.setHeader('X-MyHeader-DeviceType', 'Tablet');
}
else {
request.setHeader('X-MyHeader-DeviceType', 'Desktop');
}
}
Review the table for information about the available parameters.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| request | Request | An object representing the outgoing current request. Modifications to this request object are visible to the origin but not visible to any of the other event handlers. |
onOriginResponse
The onOriginResponse event happens as the origin response is created. The event only happens if the response is not served from cache and not constructed on the edge. Use this event if you want to modify the response before it is cached.
// remove header returned from origin
export function onOriginResponse(request, response) {
response.removeHeader('InternalDebugHeader');
}
Review the table for information about the available parameters.
onClientResponse
The onClientResponse happens before the response is sent to the client.
This example shows how to set a header before the response is sent to the client:
// add response header
export function onClientResponse(request, response) {
response.addHeader('Powered-By','Akamai EdgeWorkers');
}
Review the table for information about the available parameters.
responseProvider
The responseProvider event happens if the response is not already found in cache. This example shows how to return a response body:
//add content to the response
export function responseProvider(request) {
return Promise.resolve(createResponse(200, {}, "<html><head></head><body><p>Hello World</p></body></html>"));
}
To find more information about how EdgeWorker scripts are executed during the
responseProviderevent see Response Orchestration.
Review the table for information about the available parameters.
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| request | Request | An object representing the incoming request. Modifications to this request object are visible in the onClientResponse event handler. |
Event handler methods
View the supported HTTP methods for the EdgeWorkers event handlers.
| Event handler | Supported methods | Unsupported methods |
|---|---|---|
onOriginRequestonOriginResponseonClientResponseonClientRequestresponseProvideronBotSegmentAvailable | GET HEAD POST PUT PATCH DELETE OPTIONS (see note below) | CONNECT TRACE |
To use the OPTIONS HTTP method you need to add the
PMUSER_EW_ENABLE_OPTIONSvariable to your rule and set the value totrue. The name of the variable must be UPPERCASE.
Sub-requests support the
GET,HEAD,POST,PUT, andDELETEmethods.
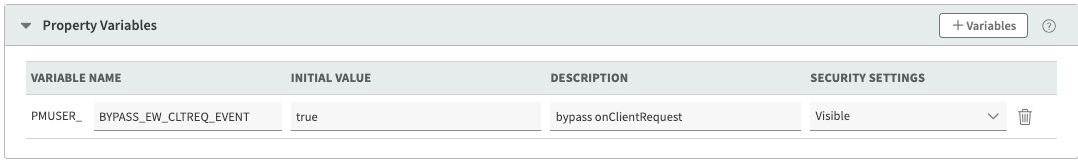
Bypass event handlers
To prevent specific event handlers from executing you can create a Property Manager variable.
Refer to this table for the PMUSER_BYPASS variable name to use for each event handler and to see the metadata stage when it's evaluated.
| Event handler | Variable name | Metadata stage evaluation |
|---|---|---|
onClientRequest | BYPASS_EW_CLTREQ_EVENT | client-request |
onOriginRequest | BYPASS_EW_ORGNREQ_EVENT | forward-request |
onOriginResponse | BYPASS_EW_ORGNRESP_EVENT | forward-response |
onClientResponse | BYPASS_EW_CLTRESP_EVENT | client-response |
responseProvider | BYPASS_EW_RP_EVENT | client-request |
onBotSegmentAvailable | BYPASS_EW_BOTSGMNT_EVENT | client-request-body or ipa-response |
To bypass an event, set the initial value of the corresponding variable to "true".
The PMUSER_ prefix for the variable is automatically included.
EdgeWorkers event handlers are always bypassed if their respective PMUSER variables are set, no matter which metadata stage they are restricted to. You can use use BYPASS variables in a programmatic manner to:
- Make decisions in later metadata stages when access to more information is available. For example, you can only execute
onClientResponseif a specific response header is present. - Set the variables from within an EdgeWorkers event, to bypass later events.
Updated about 2 months ago
